Chapter 9 Practice Problems
Answers for these practice problems are on the next page.
A good approach is to answer all of the questions on a piece of paper and then check your answers. This avoids accidentally seeing the answer(s) for questions you have not done yet.
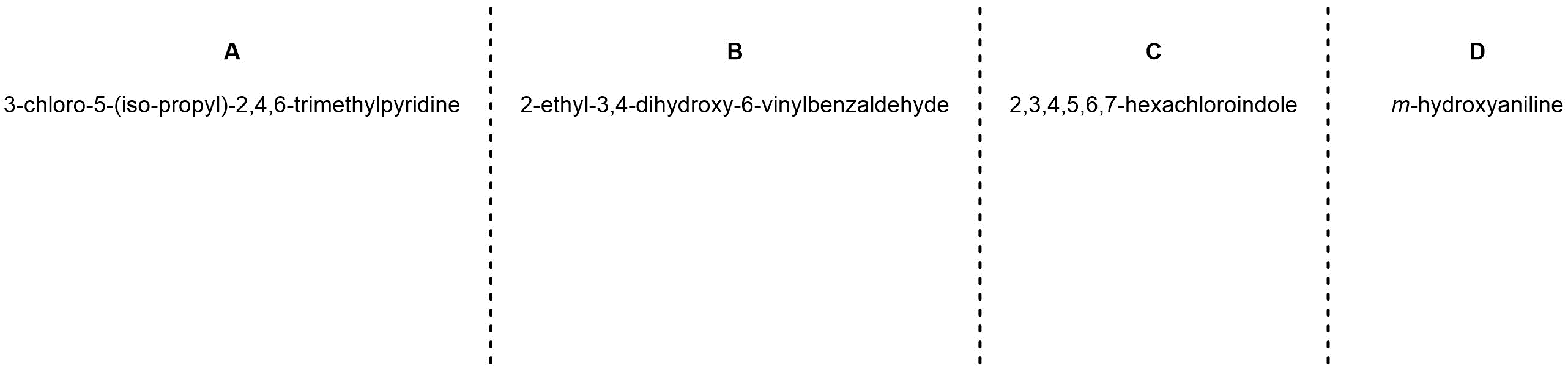
Q9.1: Class each of the following as non-aromatic or being/containing aromatic or anti-aromatic systems. If the molecule contains aromatic or anti-aromatic rings/systems circle or highlight the relevant portion(s). Assume any potentially aromatic/anti-aromatic rings/systems are planar.
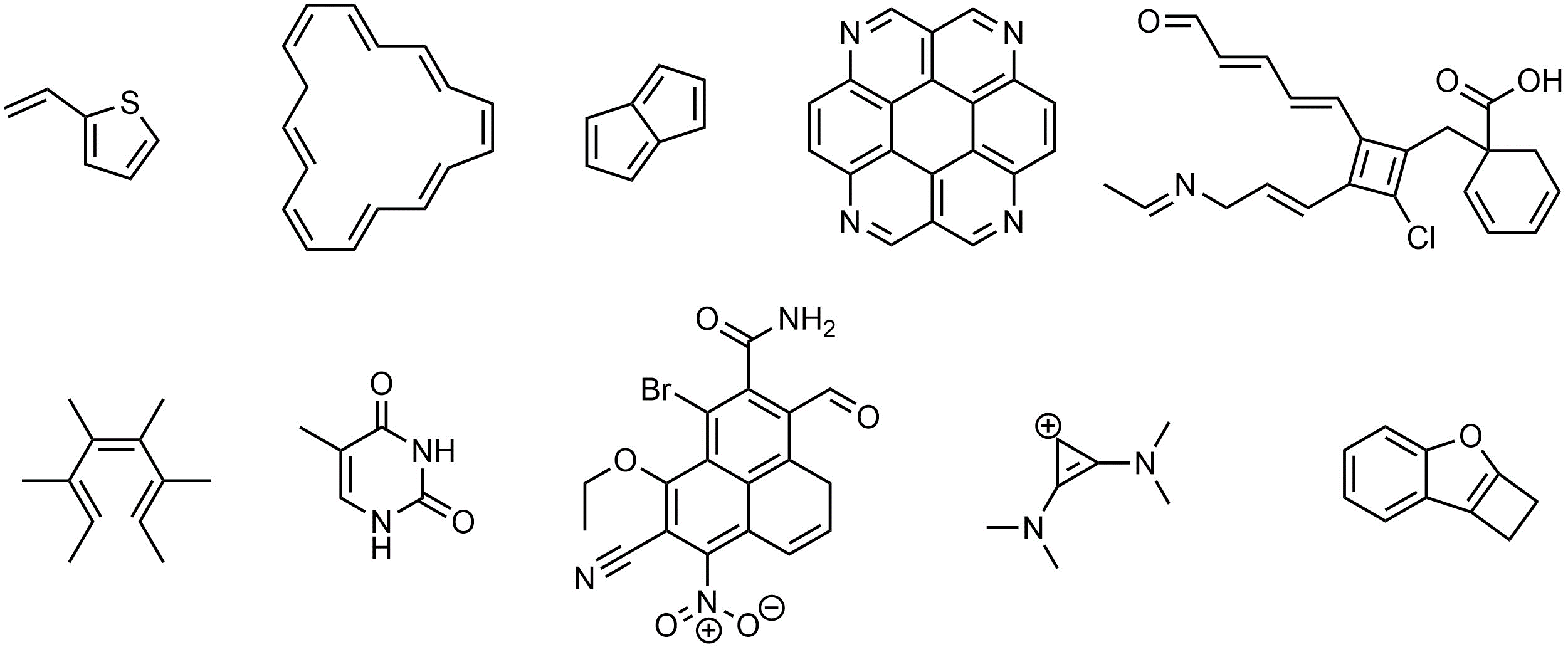
Q9.2: What is the hybridization and geometry around the highlighted atoms in these molecules? If an arrow points to a part of the molecule assume it is pointing to the carbon atom there.

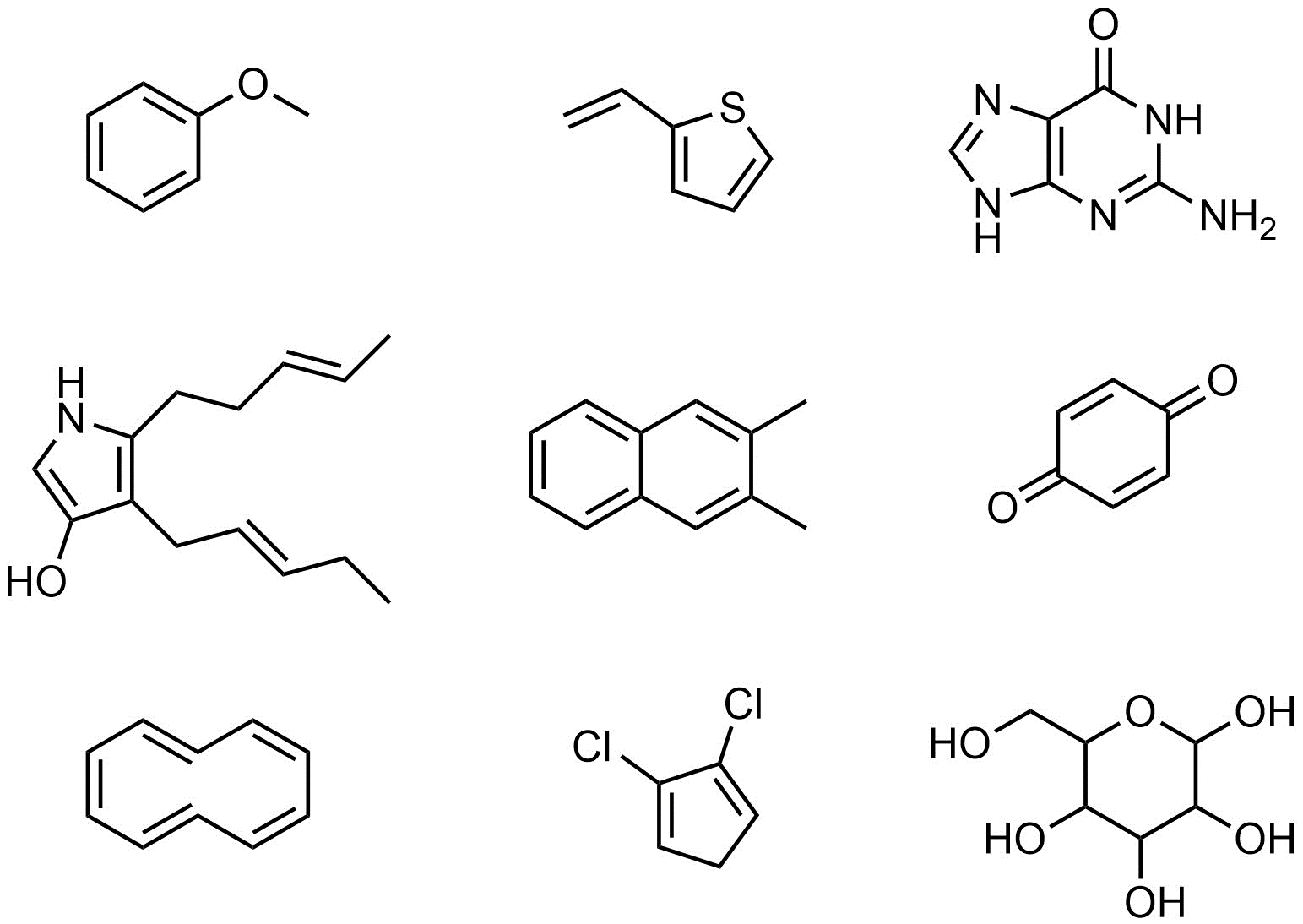
Q9.3: Amy, Bob, and Casey want to practice epoxidation reactions using mCPBA. They are willing to test out any compound as long as at least one epoxidation reaction will occur. Assume the reactions would proceed as discussed in the textbook without complications from other functional groups and that Amy, Bob, and Casey know what they are doing. Indicate (circle, highlight, draw an arrow to, etc.) all of the following molecules they should NOT try because there will be no epoxidation reaction.
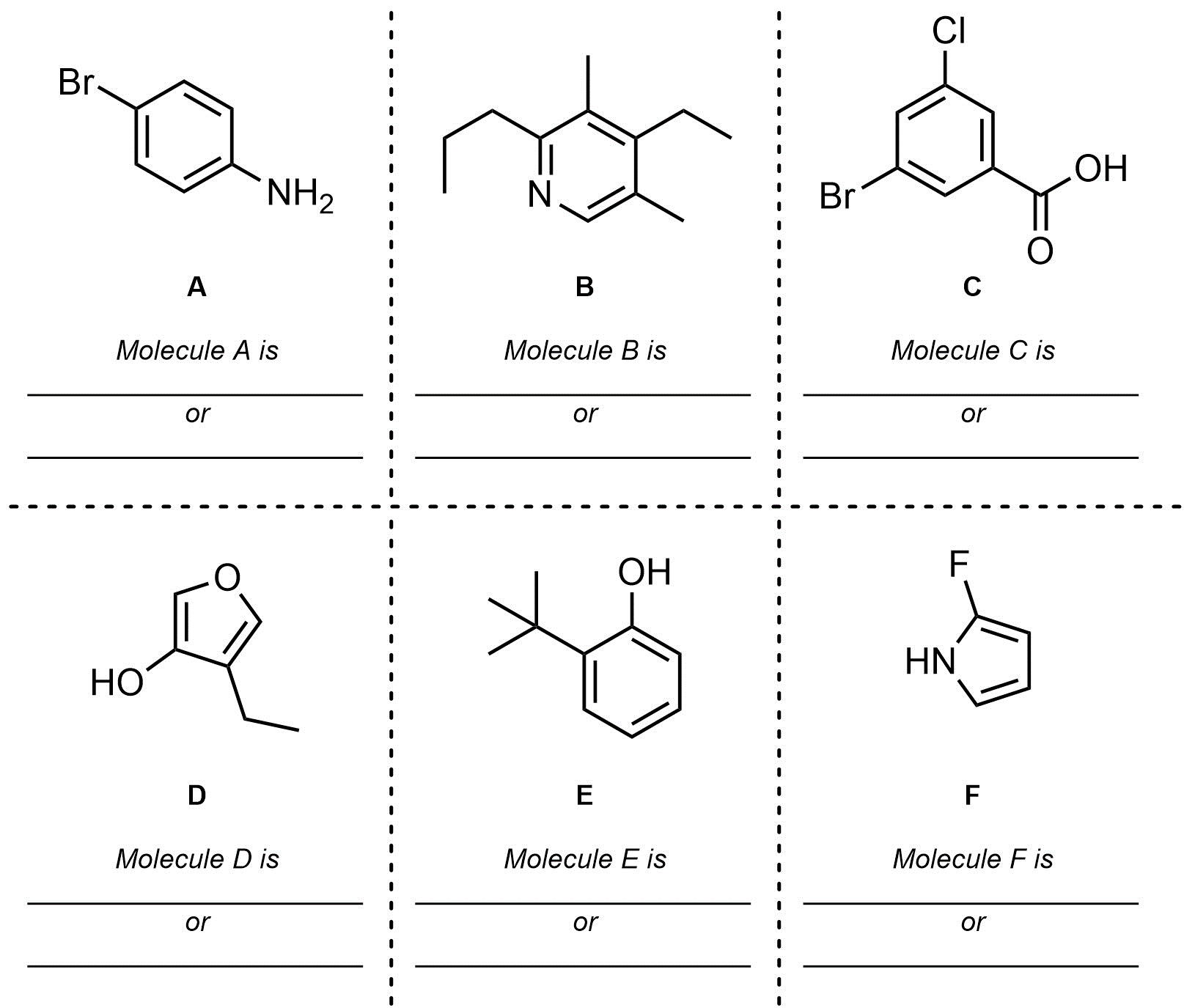
Q9.4: Name each of the following molecules using the IUPAC rules discussed in the text. Be aware that names may be (significantly) longer/shorter than the blank spaces suggest. Use the top line to name the molecule with its formal numbering. Then, if possible, add the equivalent IUPAC name using Greek descriptors (o/m/p) on the second line. If it is not possible to generate a name using the Greek descriptors indicate this in some way.
Q9.5: Draw each molecule using the provided IUPAC name.
Note: The numbering of the carbon skeleton for indoles is not straightforward and does not proceed in a simple “clockwise-around-the-ring” fashion. Think critically about where substituents must go to make a valid structure; you should not need to look up how to number indoles to generate the correct answer.