Chapter 7 Practice Problems – Answers
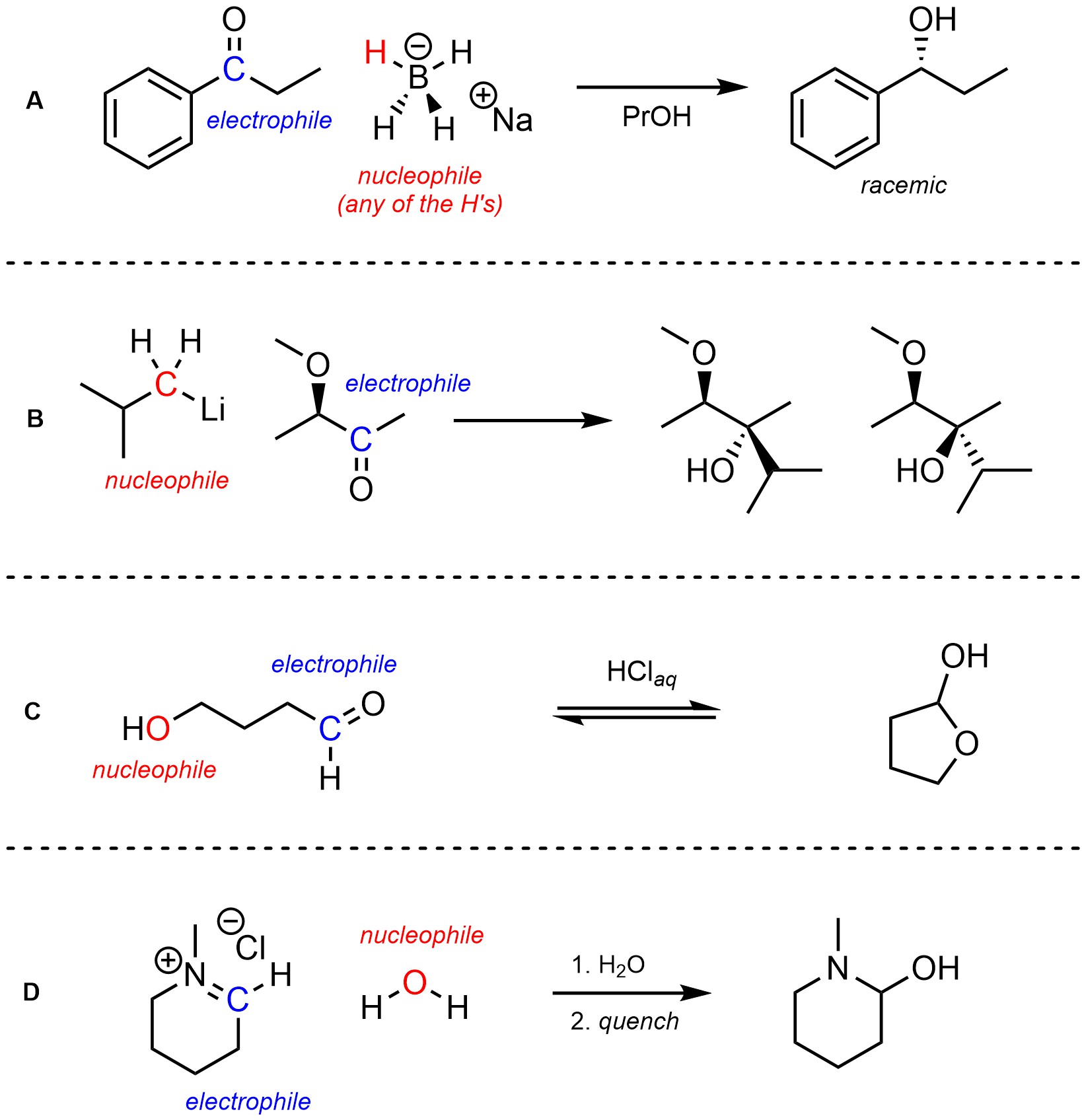
Q7.1: In each of the following reactions identify (circle and label, draw arrows to, etc.) the nucleophile and electrophile for the reaction. Indicate in some way which atoms specifically are the relevant nucleophilic and electrophilic ones for the reaction taking place.
The definitions of nucleophile and electrophile may help.
Thinking critically about
where the different parts of the product(s) come from may help.
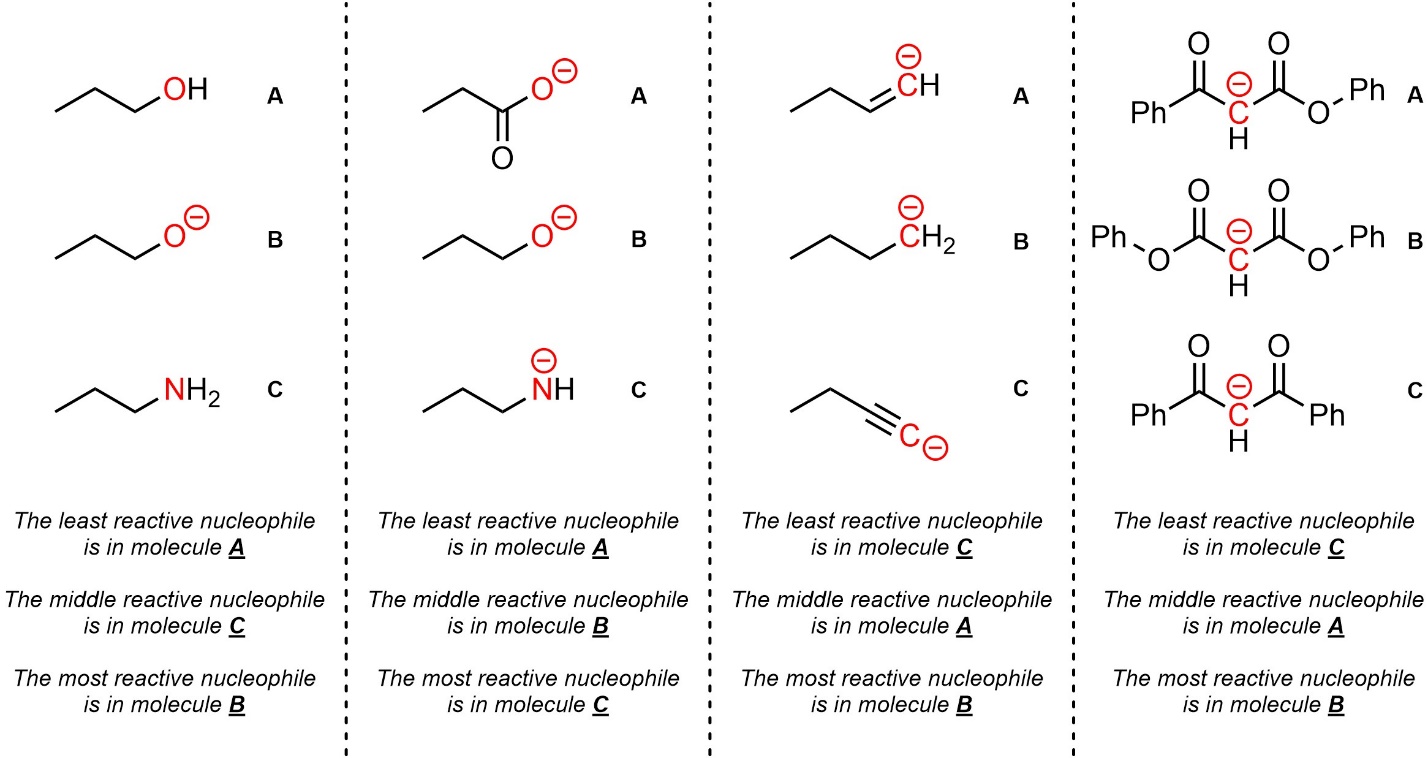
Q7.2: Rank each set of nucleophiles in increasing order of nucleophilicity (weakest to strongest). The nucleophilic atoms to consider are highlighted.
Using a pKa table might help.
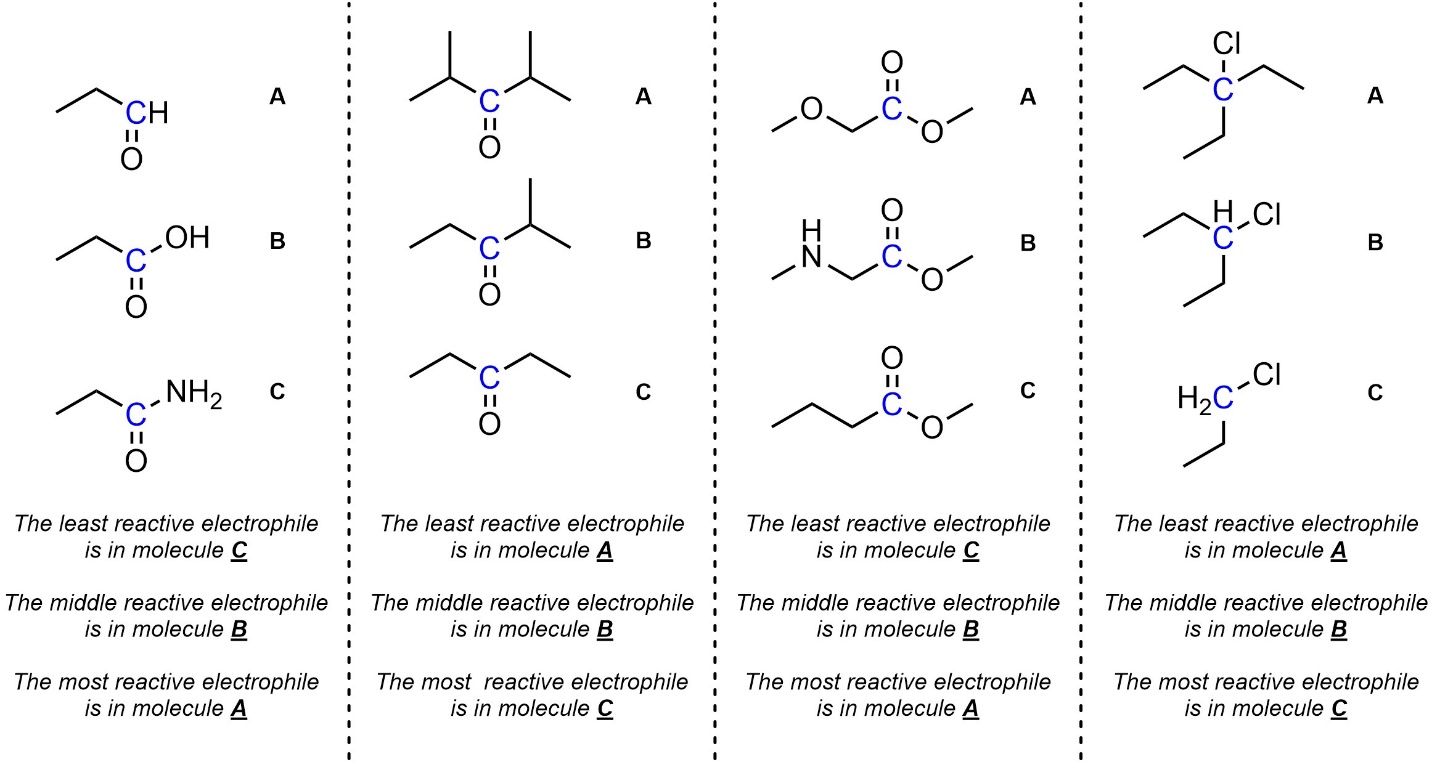
Q7.3: Rank each set of electrophiles in increasing order of reactivity (least to most). The electrophilic atoms to consider are highlighted.
Remember to consider both steric and electronic effects (Section 7.2.3).
Electrophiles do not have to be carbonyl-containing functional groups.
(coming up in later chapters)
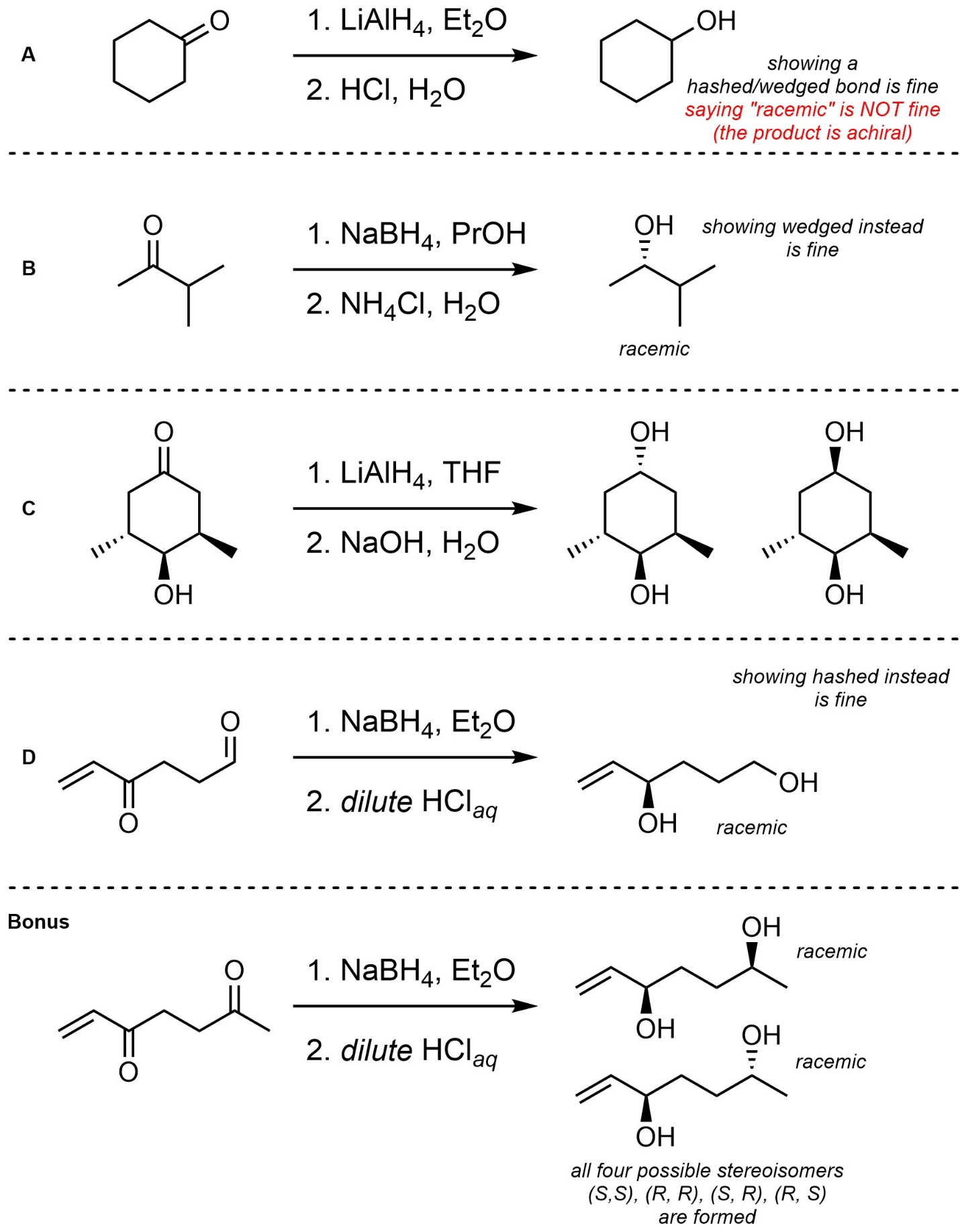
Q7.4: For each reaction, draw the expected major organic product(s). The products must be drawn as line-angle structures. Clearly indicate the appropriate stereochemistry using hashed and wedged bonds where necessary. If the product(s) is/are formed as more than one diastereomer, draw all diastereomers formed. If the product(s) is/are formed as a racemate (racemic mixture) draw only one enantiomer and write the word “racemic” beneath/beside it. Do not write “racemic” if it does not apply.
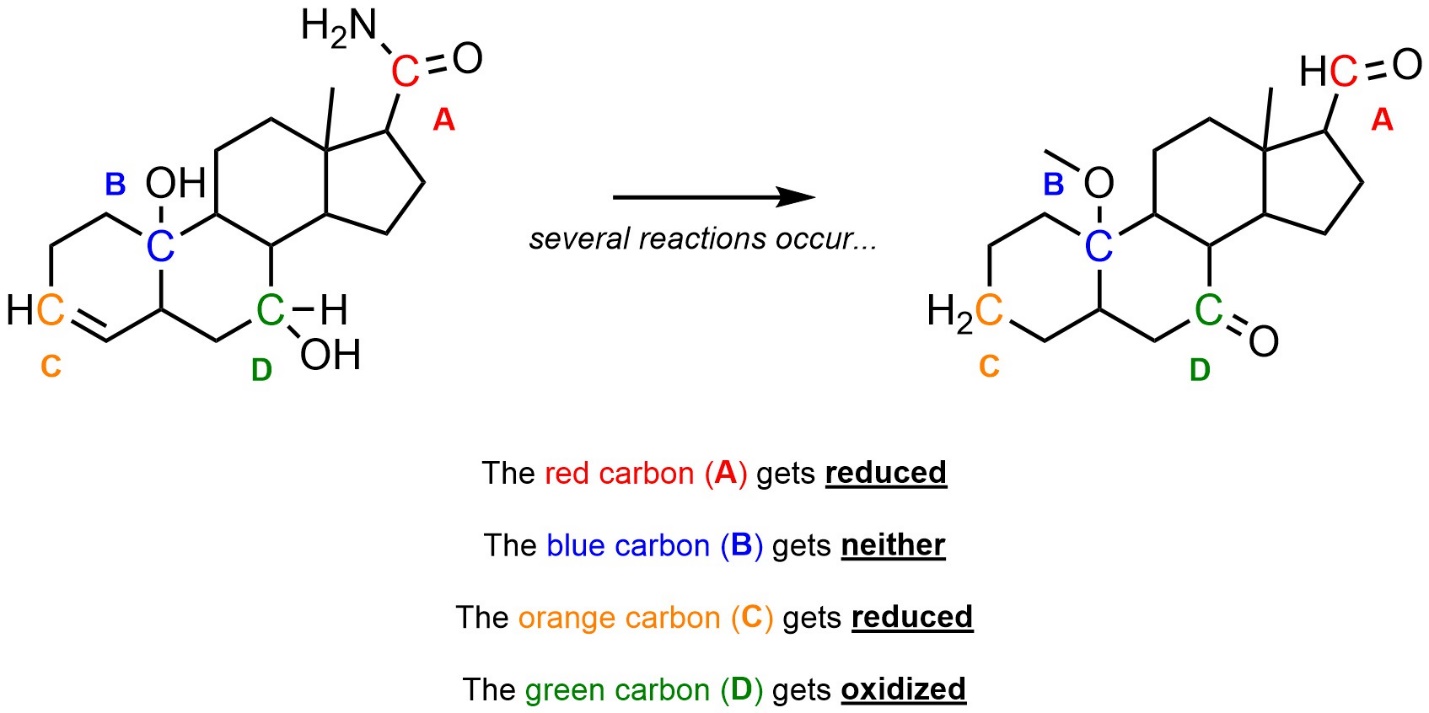
Q7.5: Class each transformation as reduction or oxidation.
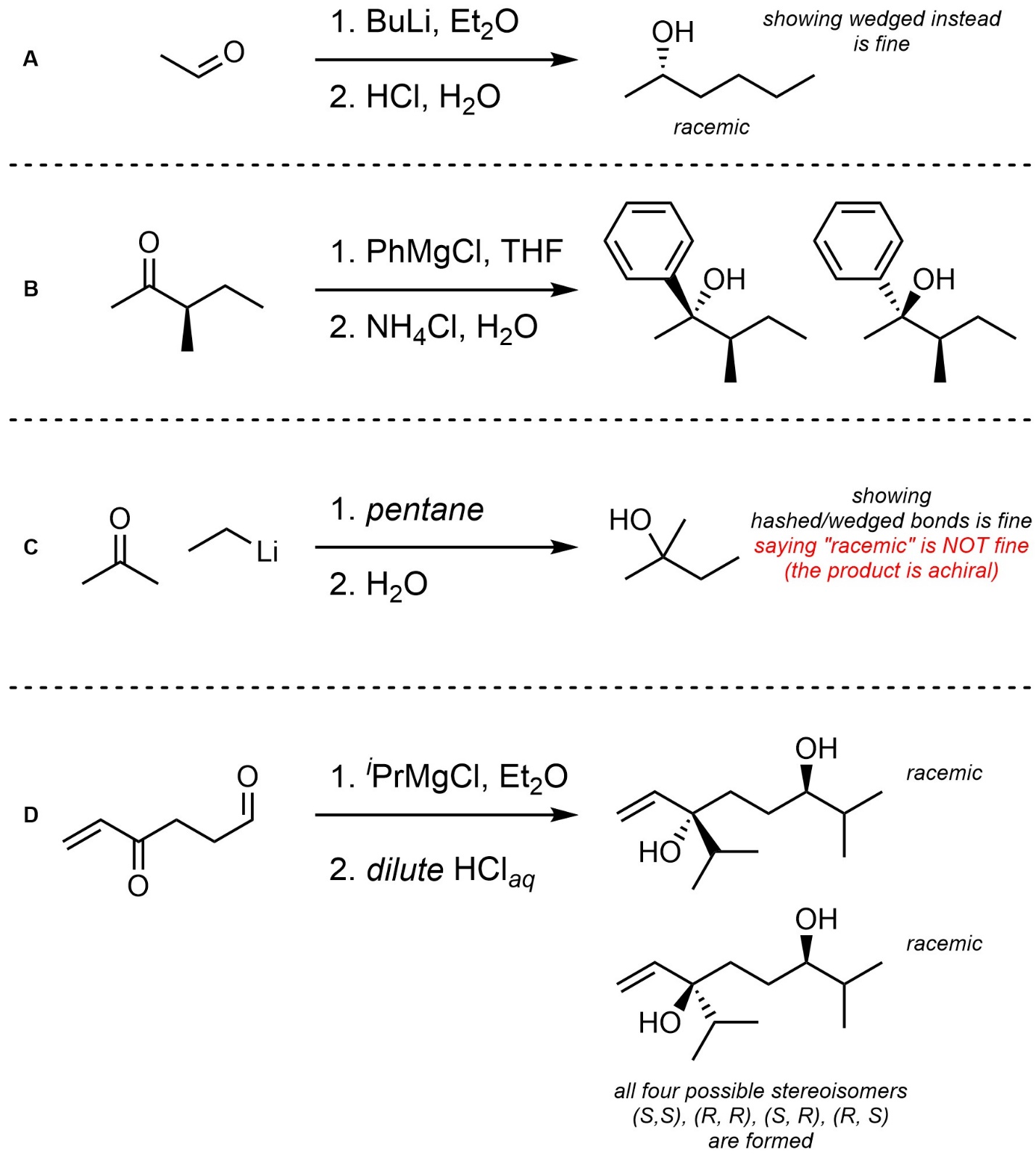
Q7.6: For each reaction, draw the expected major organic product(s). The products must be drawn as line-angle structures. Clearly indicate the appropriate stereochemistry using hashed and wedged bonds where necessary. If the product(s) is/are formed as more than one diastereomer, draw all diastereomers formed. If the product(s) is/are formed as a racemate (racemic mixture) draw only one enantiomer and write the word “racemic” beneath/beside it. Do not write “racemic” if it does not apply.
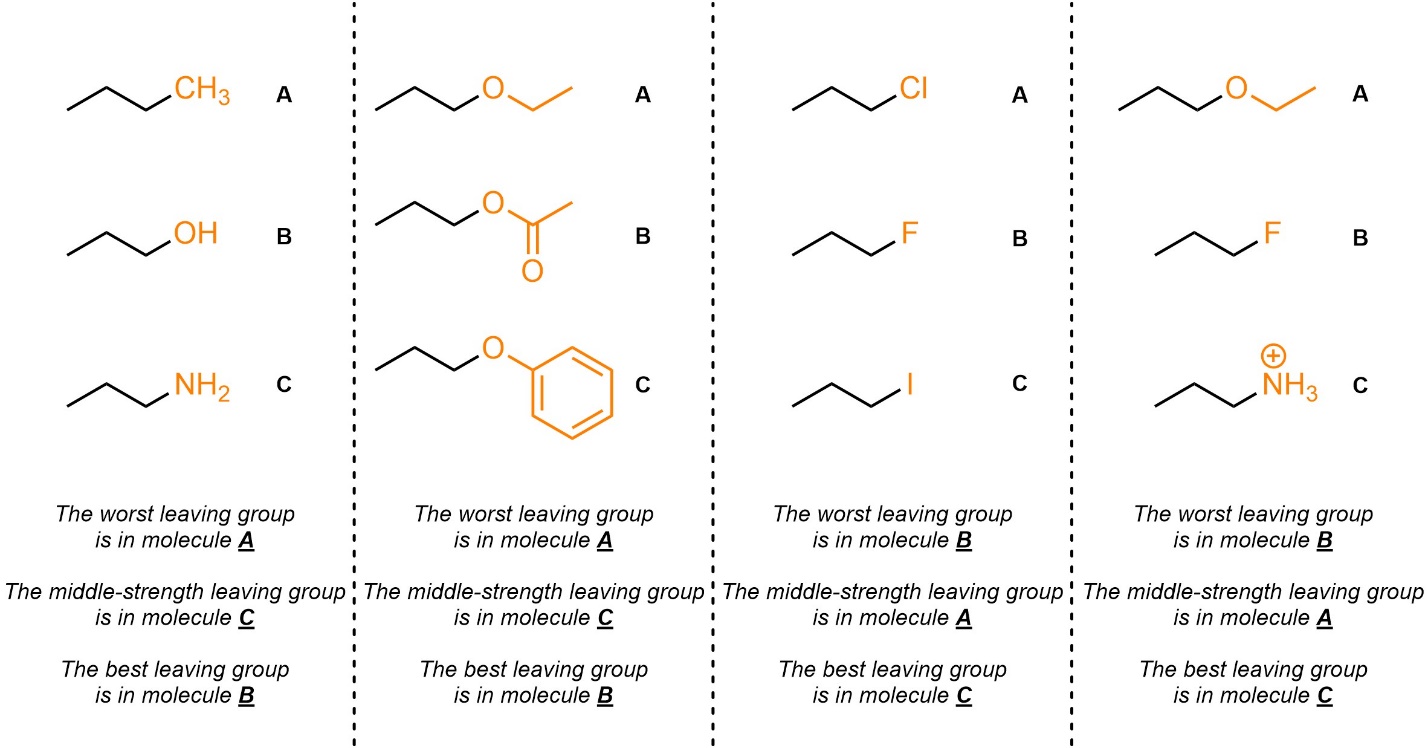
Q7.7: Rank each set of leaving groups in increasing order of leaving group ability (worst to best). The leaving groups to consider are highlighted.
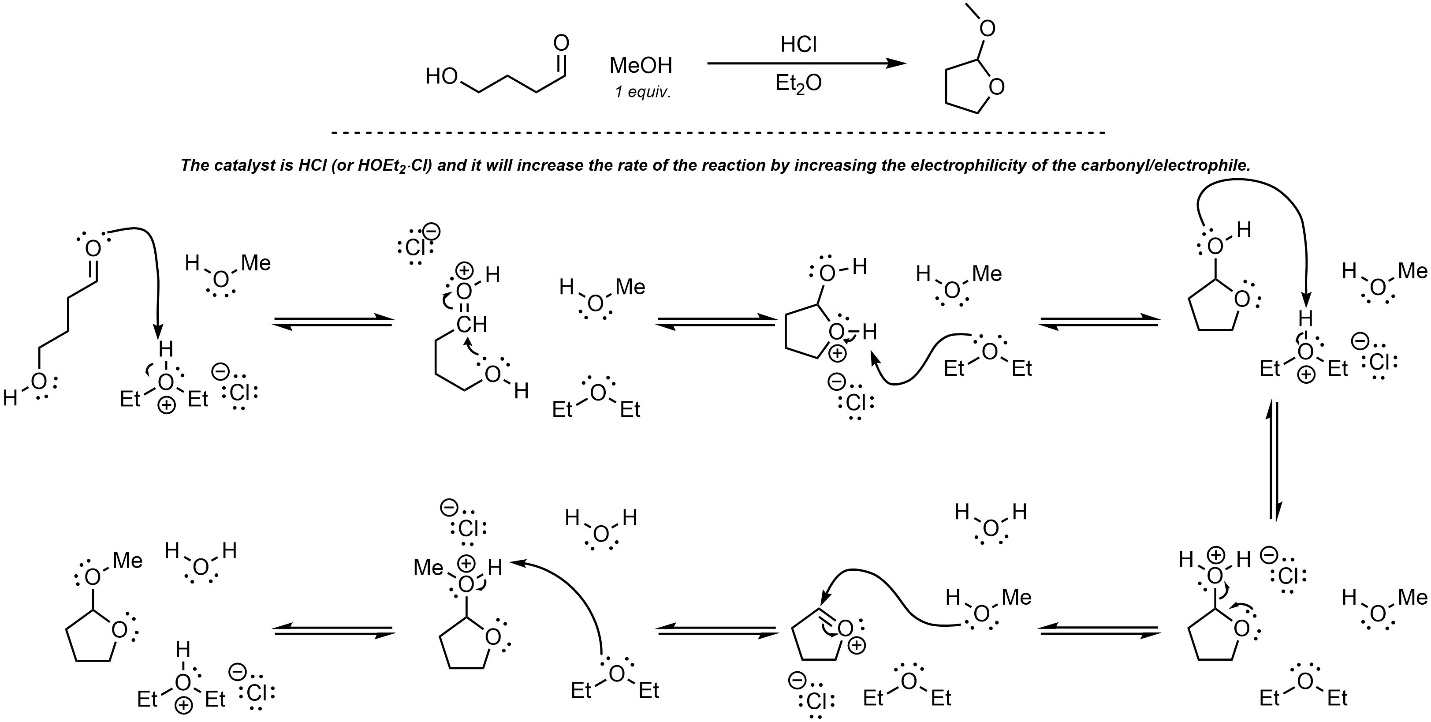
Q7.8: A reaction equation is given below. Write a brief sentence explaining which compound is the catalyst and how the catalyst will increase the reaction rate. Then propose a reasonable mechanism for the reaction. Show all necessary intermediates, curved arrows, lone pairs, and formal charges. Remember to regenerate the catalyst at the end of the reaction.
Note: For practice purposes this reaction is intentionally chosen to be challenging and have a semi-lengthy mechanism to write out. Hint: Think critically about what functional group is being made in the product.
Mechanism is the same as Scheme 7.10 in Section 7.5.3
BUT
two different alcohols add instead of two molecules of the same alcohol
and
the solvent is different
Having the methanol attack before the attached alcohol is acceptable.
(but less accurate)
Using HCl instead of HOEt2∙Cl (HCl + Et2O) as the catalyst is acceptable
but discouraged.