8.3. Weathering, Sediment, and Soil – Review Questions
- Define weathering.
- What are the main types of weathering? Describe and give examples of each type of weathering. How do the different types of weathering relate and contribute to each other?
- What are four factors that affect rock weathering rates?
- Describe the relationship between weathered particle size and surface area. Draw pictures to illustrate how weathering of a high surface area particle differs from weathering of a low surface area particle.
- In what ways does water influence chemical weathering? How does the chemistry of water influence weathering?
- How does oxygen influence chemical weathering?
- How does CO2 influence chemical weathering?
- What acid is produce when CO2 dissolves in water? How does it change the pH of water? How does it influence chemical weathering?
- How does soil affect weathering of rock?
- Give examples of Fe2+-rich rocks that can be chemically weathered and oxidized.
- Describe how weathering can affect sulfide minerals. What chemical changes happen to sulfide minerals (and water that comes in contact with them) during weathering?
- Which mineral dissolves more readily, feldspar or quartz? Why?
- what are the most common products of mineral weathering?
- What weathering products form from the minerals: feldspars, pyrite, and quartz. What type of weathering process is most important for each mineral transformation?
- Describe how the different minerals in granite weather at different rates? Which minerals alter first? Which mineral in granite is least likely to alter with weathering?
- How resistant are clays to weathering? What types of materials are rich in clays?
- How does rainfall influence weathering rates? How does temperature affect weathering rates?
- Why do we have to worry about weathering when managing mine wastes? What characteristic(s) increase weathering in mine wastes compared to ore rock?

- Point out key feature(s) in the stream shown in Figure 8.3.1 that are evidence that acid mine drainage may be present in this stream.
- Describe the process of erosion. How is erosion different from weathering?
- How do sediments change as they move over the Earths surface? What kinds of surface processes influence sediments as the move through the landscape?
- Describe how sediments are sorted and change as they move down a river that starts in the mountains and ends at a delta where the river waters enter the ocean.
- Describe how particle angularity and size can tell us about how particles have been transported. Draw pictures of particles that are (a) freshly weathered out of a source rock, (b) located in a stream few 100 km downstream from the source rock, (c) located at a beach where the stream enters the ocean.
- What are the major components of soil, in terms of types of materials that compose soil?
- How does climate influence soil formation?
- What factors influence soil formation?
- What is the relationship between soil colour and organic content?
- How do human activities influence soil erosion? Give some examples of where human activities are influencing soil erosion.
-
Draw and label a cross-section diagram illustrating a soil profile. Describe in general terms how the soil profile changes with depth.
Extra review questions that may be covered in lecture (depending on your professor) that are not completely covered in the the textbook readings:
- How does karst topography form? What type(s) of weathering is/are responsible for karst topography forming?
- Name some soil inputs, and outputs.
- Describe three ways chemical weathering affects silicate minerals.
- What factors influence mineral solubility?
- Which is more soluble, quartz or halite? If you increased the temperature and pressure, would quartz be more or less soluble?
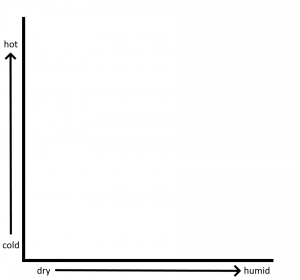
- What kinds of weathering are common in arid regions? In humid regions? In hot regions? In cold regions? Fill in the diagram below to show how the amount of chemical and physical weathering varies with climate conditions.
- What are the functions of soil?