Chapter 16 – Urogenital
Hematuria
ACR – Urologic – Hematuria
Case
Transitional Cell Carcinoma
Clinical:
History – Macroscopic hematuria.
Symptoms – This 66 year old female reported macroscopic hematuria. She also feels that she is not completely emptying her bladder.
Physical – None
DDx:
Cystitis
Bladder mass
Bladder dystonia
Imaging Recommendation
ACR – Urologic – Hematuria, Variant 3
CT Abdomen and Pelvis
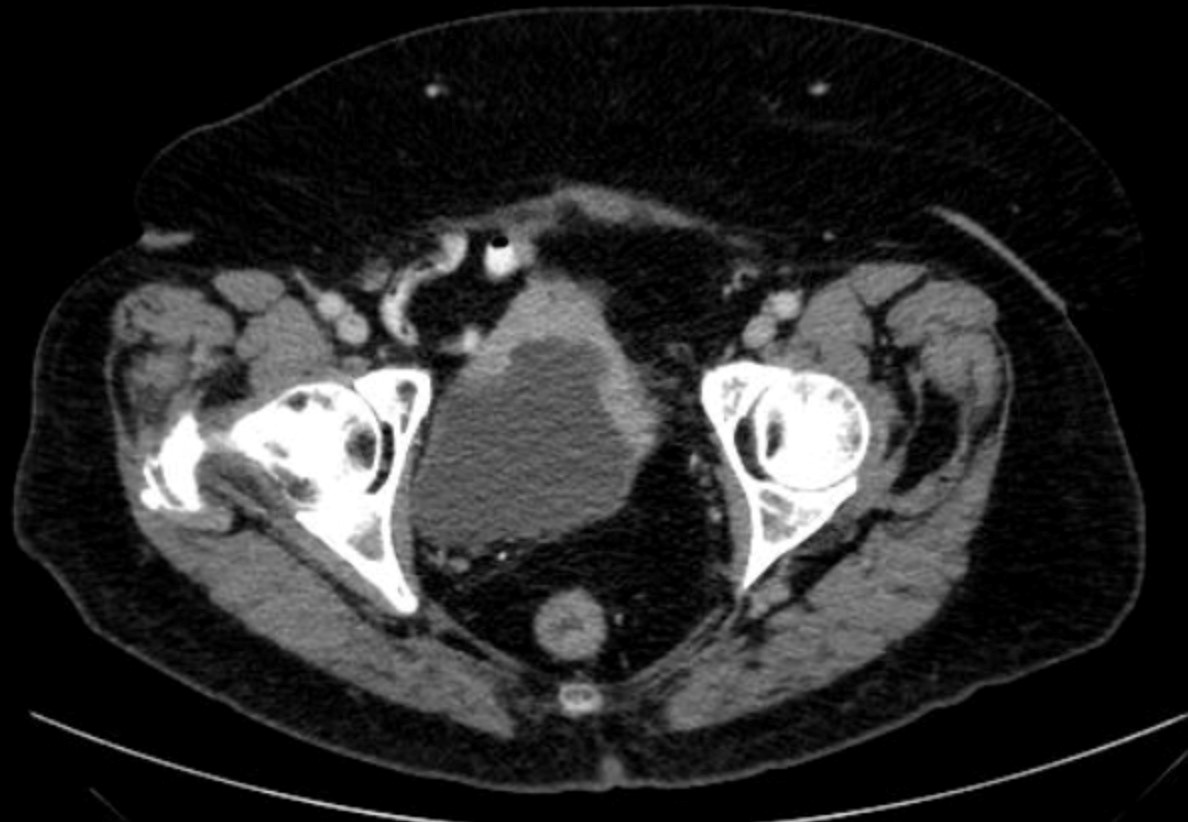
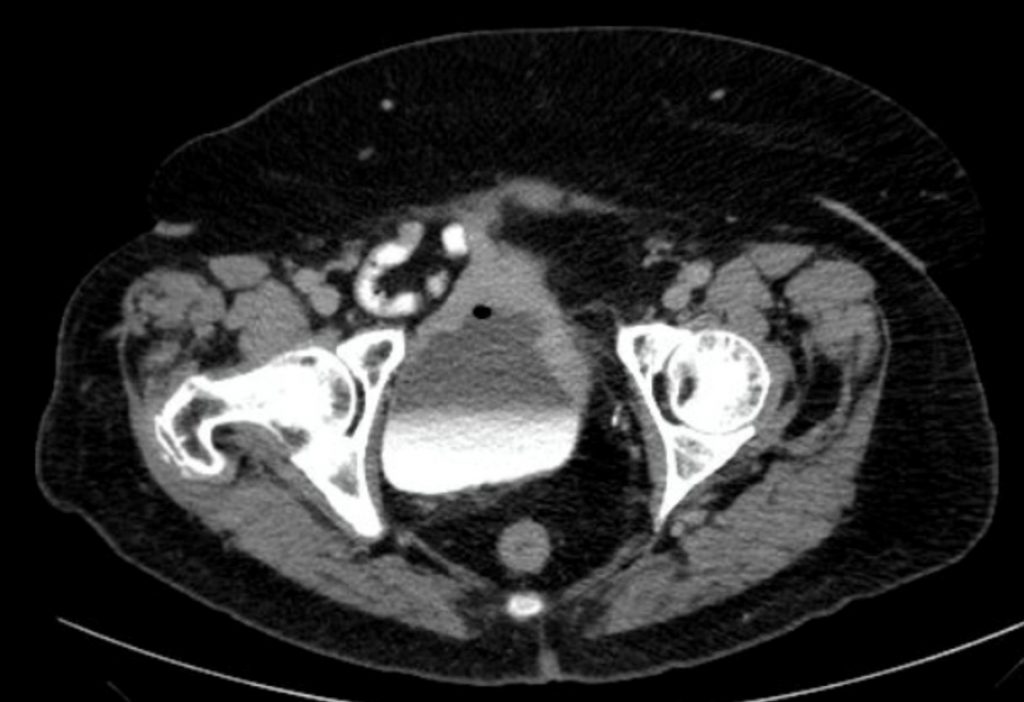
Imaging Assessment
Findings:
The CT revealed a thick, irregular, ventral wall of the bladder. This thick wall contrast enhanced. No other findings.
Interpretation:
Bladder wall mass
Diagnosis:
Transitional Cell Carcinoma – Biopsy proven
Discussion
Hematuria is one of the most common presentations of patients with urinary tract diseases and of patients referred for urinary imaging. This discussion describes a radiologic approach to such patients. It is limited to adults and does not refer to patients whose hematuria coexists with other clinical situations reviewed in other ACR Appropriateness Criteria® topics, including acute trauma, infection, renal failure, symptoms of acute stone disease, known renal masses, and prostatism.
The initial decision to be made is whether all patients with any degree of hematuria need imaging evaluation. Hematuria can originate from any site in the urinary tract but can be roughly divided into renal, urothelial, or prostatic causes. Thorough evaluation of gross hematuria is recommended, and this is usually done with a combination of clinical examination, cystoscopic evaluation, and urinary tract imaging. Patients on anticoagulants who present with gross or microscopic hematuria have a sufficiently high prevalence of important diseases including renal and uroepithelial tumors that workup cannot be forgone.
The imaging evaluation will almost always be accompanied by cystoscopy to evaluate the urinary bladder, since many bleeding urinary tract lesions arise in the urinary bladder, and imaging procedures are not yet conclusively proven to be as sensitive as cystoscopy in diagnosing most of them. Multi-detector-row computed tomography (CT) has been evaluated in detecting bladder cancers, and reports suggest a sensitivity and specificity of 95% and 92%, respectively. One retrospective study reports that computed tomography urography (CTU) and cystoscopy had similar diagnostic accuracy for detection of bladder cancer in patients with hematuria alone; however, cystoscopy remains superior in patients with prior urothelial malignancy.
Computed Tomography
Until the mid -1990’s, excretory urography (IVU) was the imaging study used in evaluating hematuria, but development of multidetector CT and the excretory phase CT urogram, also known as CTU, have supplanted IVU over the past 15 years.
Attributions
Figure 16.3A Axial CT of the pelvis without contrast. The bladder wall was thickened by Dr. Brent Burbridge MD, FRCPC, University Medical Imaging Consultants, College of Medicine, University of Saskatchewan is used under a CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
Figure 16.3B Axial CT of the pelvis with contrast demonstrating the bladder wall mass by Dr. Brent Burbridge MD, FRCPC, University Medical Imaging Consultants, College of Medicine, University of Saskatchewan is used under a CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.

