Chapter 8 – Cardiovascular
Enlarged Cardiac Silhouette
Case
Enlargement of the Cardiac Silhouette, Cause Not Yet Diagnosed
Clinical:
History: This patient presented for an Annual Physical Examination. Mild hypertension for 5 years, medicated.
Symptoms: None
Signs: Chest palpation suggested cardiac enlargement. A quiet diastolic murmur was heard.
DDx:
Cardiac – valvular, ischemic, cardiomyopathy
Epicardial – effusion
Extracardiac – fat, mass, fluid, pectus excavatum
Poor Inspiration
Portable imaging technique
Imaging Recommendation
Chest x-ray
ODIN Link for Enlarged Cardiac Silhouette images: https://mistr.usask.ca/odin/?caseID=20160107114411264
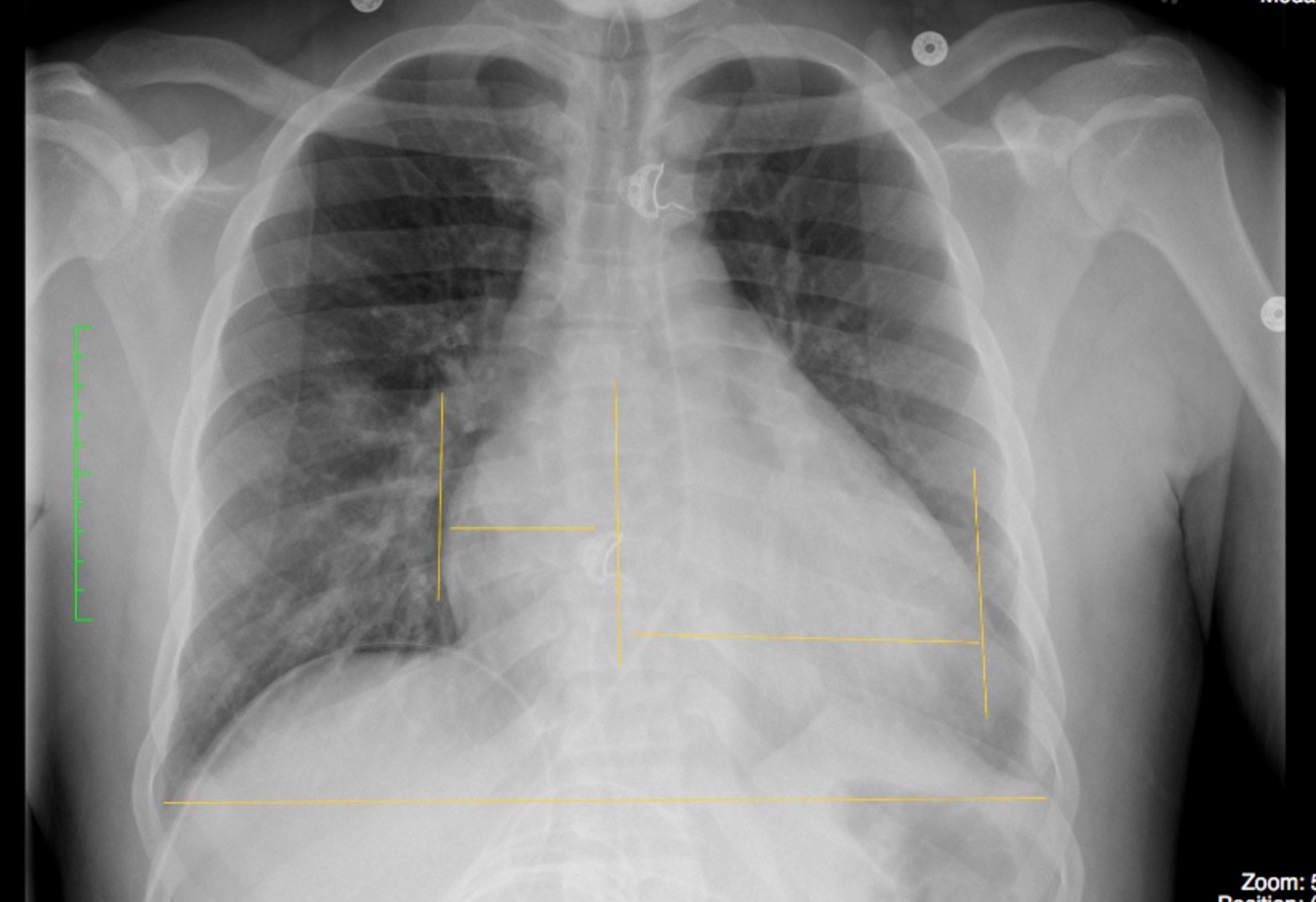
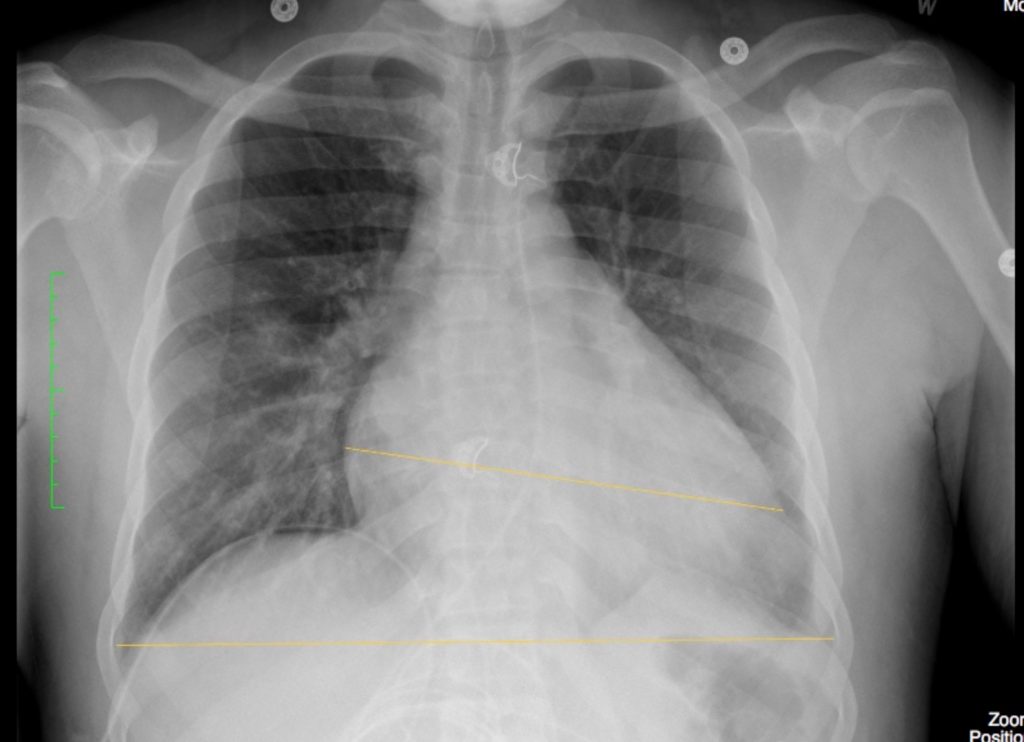
Image Assessment
Findings:
The cardiac silhouette was enlarged. The Cardio-Thoracic Ratio (CTR) measured 31/50 cm – 62%. A normal ratio should be less than 50%.
The lungs and pleural spaces were clear. No evidence of alveolar or interstitial edema. No evidence of aortic or coronary artery calcification.
Interpretation:
Enlargement of the cardiac silhouette requiring further investigation. Further investigation with ECG, and Echocardiography, were pending.
Diagnosis:
Enlargement of the Cardiac Silhouette, Cause Not Yet Diagnosed
Discussion:
Potential causes of Enlargement of the Cardiac Silhouette include:
a) Cardiac chamber(s) (atria, ventricles) – related to valvular disease or cardiomyopathy (ischemic, dilated), congenital heart anomalies, other
b) Pericardium – pericardial effusion, pericardial tumor
c) Epicardial – fat, tumor
d) Anterior Mediastinal mass
e) Expiratory phase x-ray
f) PA – Portable x-ray technique
Hence, further history, acquisition of old imaging and subsequent further testing, including imaging, will be required.
Attributions
Figure 8.3A Chest x-ray with an enlarged heart shadow by Dr. Brent Burbridge MD, FRCPC, University Medical Imaging Consultants, College of Medicine, University of Saskatchewan is used under a CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
Figure 8.3B Chest x-ray with an enlarged heart shadow by Dr. Brent Burbridge MD, FRCPC, University Medical Imaging Consultants, College of Medicine, University of Saskatchewan is used under a CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.

