12 Leveraging ChatGPT as a Teacher and Student Resource
Matthew Washlowsky

Image created with Midjourney AI image generator.
Prompt: A high school student looking at a computer screen and having a conversation with Chat GPT. There should be word bubbles and text in the image.
Introduction
ChatGPT is a language model developed by the artificial intelligence research team at OpenAI. It is designed to generate human-like text in response to input prompts it receives from the user. ChatGPT was developed through training on a massive amount of text and conversation through various sources. The full methodology is available on ChatGPT’s website.
When the user provides an input prompt, ChatGPT is capable of understanding and outputting text in a mostly coherent and contextually relevant manner. Due to its popularity, it has become renown as the posterchild of AI and is useful for a variety of tasks, including:
- answering questions
- generating content
- providing explanations
- computing complex conversations
- and engaging in conversation
For some perspective, much of the introduction to the tool was developed based on ChatGPT’s self-explanation (see Figure 2 below).
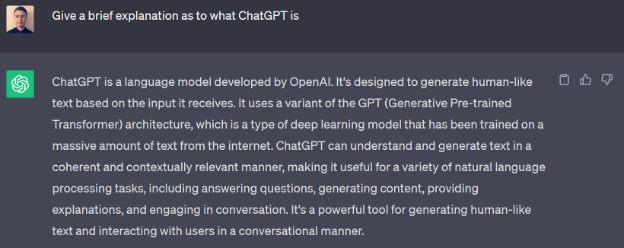
Figure 2. A screenshot of a prompt given to OpenAI’s ChatGPT v3.5 on August 20, 2023.
Critical Media Literacy (connection to Curriculum)
ChatGPT has been a controversial tool for both education and businesses. As a comprehensive input and output AI, it is a modern form of Pandora’s Box that significantly impacts the day-to-day of many. Just as the internet, google, smartphones, social media, and other technological tools have impacted education, so too will ChatGPT. Now that the box has been opened, it is the responsibility of educators to emulate responsible and respectful use of the tool.
Saskatchewan secondary English Language Arts (ELA) curriculum directly states that “[ELA is about] using contemporary technologies to learn and to document understanding.” Even at the twelfth-grade level of ELA, the curriculums states that students shall “use a variety of technologies to facilitate and enhance representation including computer software and multimedia technology” and “Use technology as a tool to research, organize, evaluate, and communicate information, and demonstrate a fundamental understanding of the ethical and legal issues surrounding the access and use of information” (Saskatchewan Ministry of Education, 2013).
Even at the elementary level, it is expected that students will “need to consider the role of communication in their lives and the technologies and strategies that help people become effective communicators.” All curriculum within Saskatchewan contains three broad areas of learning that reflects Saskatchewan’s goals of education. All three can be supported directly through various activities using ChatGPT or other AI conversation devices. The three broad areas of learning are:
- To become lifelong learners
- To gain a sense of self, community, and place
- To become an engaged citizen
Affordances and Constraints

Figure 3 “Opening Pandora’s Box” by Midjourney AI – Generated August 21, 2023
One of the many concerns through academia, especially in the post-secondary level, is that of using these tools to cheat, plagiarize, and violate ethical standards. ChatGPT is not the first website on the internet to cause difficulties for these institutions. Websites such as Chegg, SparkNotes, Wikipedia, essay-writing services, and Course Hero are all examples of previous resources that students have abused in the past. And in all cases, precautions have been put in place to limit their impact to academic standards.
While AI with free services such as ChatGPT cause large concerns, institutions are now taking steps to limit the impact of such abuses. Recall that ChatGPT is at the simplest form, and input and output advice. It cannot make new and original pieces of content. Rather, it scours its database – namely, the internet – and combines pieces from several sources. As such, it is relatively easy to detect through plagiarism detectors such as Grammarly, plagiarismdetector, duplichecker, and many more.

Figure 4 “GPTZero” logo
Another flaw with ChatGPT’s writing is that unless the cheater completes a comprehensive re-write of the material output, the essay will simply not flow well and will provide several unnatural sentences or phrases. A new tool, GPTZero, is an app designed to detect whether an essay in written by ChatGPT or by a human. Taking the output of ChatGPT from Figure 2, for example, will indicate a 52% probability that the text was entirely written by AI (which in this case, it was).
When ChatGPT was asked the following prompt about George Orwell’s Animal Farm:
“Some critics believe that, at the end of the book, Orwell suggests that the pigs and human political leaders are interchangeable. Do you think most government rulers are interchangeable? How might power change those who have it? Explain.”
The outputted essay was found to be 74% written entirely by AI. The only non-plagiarized section was the first paragraph, which simply re-worded the prompt.
Pandora’s box has opened. The New York Times headlines an article with the same logic that the world of education should have today: “Don’t Ban ChatGPT in Schools. Teach With It” (2023).
Possibilities of ChatGPT in Education
| Themes | Teacher Uses | Student Uses |
| Generating Ideas |
|
|
| Generating items |
|
|
Teacher uses:
One of the foundational elements of undergoing teacher training programs within Saskatchewan is reflecting on practice, sharing resources, professional development, and meeting students where they are. In an ever-increasing landscape of large class sizes, wide teacher portfolios, heavy workloads, and in some cases teaching unfamiliar subjects, chat GPT becomes a useful tool for teachers.
An immediate use for the tool is to simply generate ideas or resources for the classroom. Whether it’s brainstorming ideas and creating lesson plans, suggesting teaching strategies, or giving prompts for lesson/unit goals.
Example teacher prompts:
- Make a unit plan for teaching Romeo and Juliet to grade nine students.
- Generate 20-word problems that require factorizing binomials for grade ten students.
- Give me ten grade-twelve essay prompts for Lord of the Flies?
- What are some ways I can teach grade five students about conflict resolution?
- Can you make me a 1-page reading for grade four students about this?
- Provide me a list of teacher professional development resources to help me better teach struggling students.
- Give me the five best resources about the dangers of TikTok. They should be age-appropriate for grade six students.
- Provide three important questions that my students need to answer while they read one of these articles.
- Generate an answer key on these three questions.
- Create a grade-nine level sample of a short response about the responsibilities of the government.
- How can I professionally state in an email that your son is causing inappropriate distractions that are hindering the rest of the learners from accomplishing the goals of our lessons?
- Provide me a grading rubric for a group PowerPoint presentation. The presentations involve three grade-six students researching and presenting on different plants that are indigenous to central Canada.
- The language in the rubric is too complicated for sixth graders. Please simplify it.
- Generate a sample five-page essay on hurricanes that have some grammatical errors.
- Show me the answer key.
Student-uses:
If one was to question any current teacher of middle/secondary students about their thoughts of how students interact with search engines such as Google, they would probably be met with dismay. A common theme tends to be a blind trust regarding the first option that Google spits out, with no deeper research into whether the information is accurate or investigation into the context of the answer. Inputting the same prompt into ChatGPT may offer a more substantial reasoning behind the question and allows the student to offer follow-up questions and prompts.
Students can benefit from using ChatGPT individually as a study-tool and in-class. It can offer immediate assistance with coursework or assignments, it can give them ideas for essays or presentations, it can help them translate text, provide explanation for how-to-do tasks, improve writing skills, create flashcards, proof-read text, and correct grammar.
Example student-prompts:
- Explain the concept of photosynthesis in simple terms.
- Help me with my social studies paper on the Canadian confederacy.
- What are some topics I can write on?
- What are some authentic sources I can start with?
- Can you pretend to be Hamlet for the conversation? I need to interview you.
- I need ideas for my science assignment on renewable energy.
- Here is my current essay. What are some ways I can improve it?
- Help me solve the following math problem. Give me a step-by-step solution and explanation.
- “Find the equation of the line that passes through the points (-1 , -1) and (-1 , 2).”
- How do I put a YouTube video into my PowerPoint? I want it to autoplay.
- Give me flashcards for my health studies test. It needs to be about human anatomy.
- Give me more and make them harder.
- Make a step-by-step guide for creating a simple website.
- Explain the supply and demand with real-world examples.
- How can I ask my teacher for an extension?
- How do I source a YouTube video?
The Process
Using ChatGPT is a very simple process. While paid services are available, ChatGPT version 3.5 is available for free and is competent for most uses. To gain access to the service one should follow the instructions below:
Making an Account:
Step 1: Go to https://chat.openai.com/
Step 2: Create an account under “sign up” with an email address.
Step 3: Verify your email.
Step 4: Input information about yourself
Step 5: Verify your phone number.
Using ChatGPT:
Step 6: Inputting prompts is a very simple process. Simply input a prompt at the bottom (see figure 4) and press the green button to proceed.
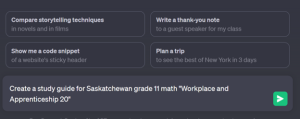
Figure 4 – ChatGPT Prompts
Step 7: ChatGPT will then output a response. You have the choice of continuing the dialogue in that thread or creating a “New chat” on the top left corner.
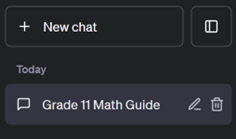
Figure 5 – ChatGPT Threads
Prompt Engineering
All prompts are not equal. If low-quality inputs are put into ChatGPT, you may get low-quality outputs out of ChatGPT. Providing more detail and specifics may lead to a product that aligns closer to your vision. In some cases, ChatGPT will become unable to respond to certain prompts due to code of conduct reasons or because it is outside of its abilities. Simply rewording your statements may yield the AI to respond.
Some generation recommendations on improving prompt engineering for ChatGPT are as follows:
- Providing specific prompts.
- Include details such as the anticipated age/grade range the materials are for
- Specify what format you want.
- Avoid vague prompts.
- Establish a thread and use context.
- Inputting background information into ChatGPT before your primary prompt can add context for when the AI searches for results.
- Keeping each thread to a specific topic – for example, a grade seven ELA thread – can help the AI keep track of your expectations from previous requests.
- Alec Couros recommends the following prompt template: “Act as [role]. I will provide you with [information on input]. You will [detailed task]”
- Specify sources.
- Should the information come from scientific journals? Do you want to avoid YouTube and Wikipedia? Be explicit.
- Let the AI search its full database.
- Ask open-ended questions instead of yes/no questions. Prompts staring with “how,” “why,” “explain,” and “provide a step-by-step on,” will elicit better results.
- Ask for a specific number of outputs, for example, “list the top 10 reasons why…” as a prompt.
- Allow the AI to get creative. Prompts such as “imagine a situation where…” can provide unforeseen outputs.
- Experiment with your prompts
- A prompt can always be improved upon. If you do not like certain outputs of ChatGPT, specify which ones and ask for a re-attempt or adjust your input prompt. Adding in additional context may also be beneficial.
Alec Couros (2023) also provided the following prompts in his presentation on ChatGPT. If one examines the “example prompt” column, they will notice that the prompts are very specific and often include open-ended questions with deep explanations within the prompt.
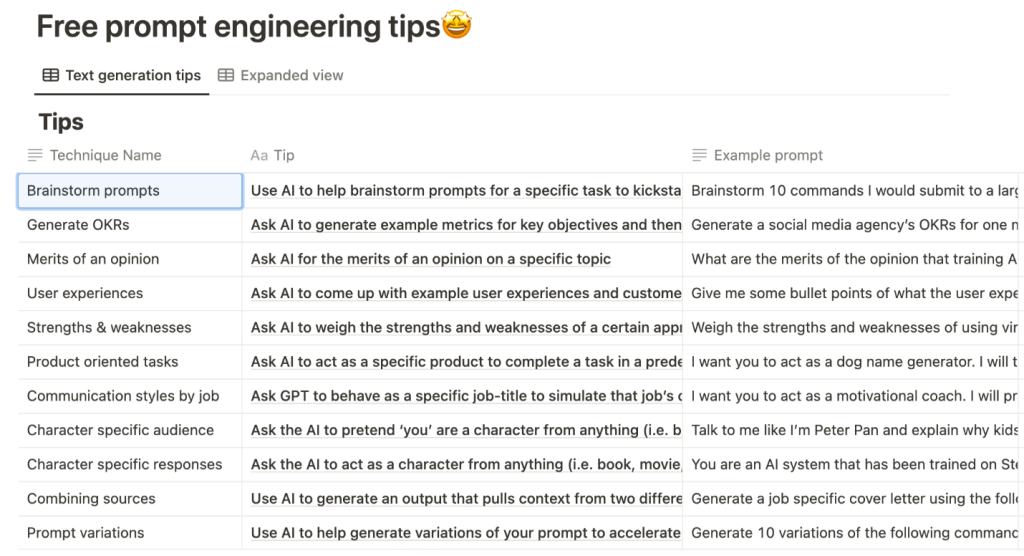
Figure 4. Prompt Engineering Tips suggested by Alec Couros (2023).
Informative presentation
Click the image above for A Brief Overview of ChatGPT 3.5 for Educators
References
ChatGPT: A New Tool for Schools, but Will Teachers Use It?” The New York Times, 12 January 2023, www.nytimes.com/2023/01/12/technology/chatgpt-schools-teachers.html
Couros, A. (2023, January 13). Let’s Talk About Teaching & Learning. Presentation at University of Regina,
Holz, D. (2023). Midjourney. https://www.midjourney.com/
Saskatchewan Ministry of Education. (2009). Saskatchewan Social Studies 9 Curriculum. https://curriculum.gov.sk.ca/
Saskatchewan Ministry of Education. (2010). Saskatchewan English Language Arts 5 Curriculum. https://curriculum.gov.sk.ca/
Saskatchewan Ministry of Education. (2013). Saskatchewan English Language Arts 30 Curriculum. https://curriculum.gov.sk.ca/
OpenAI. (2022, November 30). ChatGPT. https://www.openai.com/research/chatgpt
Tian, E. & Cui, A. (2022). Towards detection of AI-generated text using zero-shot and supervised methods. GPTZero. https://gptzero.me/

