15 Motivation Magic: Using Canva Magic Studio to Boost Motivation
Kendra Hart
Abstract
This chapter explores the use of Canva Magic Studio, an AI-powered design toolkit, to enhance motivation in the classroom. Features to support visual design, writing, and media creation empower educators to create engaging and visually interesting learning materials. The ARCS Model of Instructional Design is outlined to illustrate how Canva Magic Studio tools support learners in the realms of attention, relevance, confidence, and satisfaction. Practical tips for the implementation of Canva Magic Studio in learning communities are proposed, and ethical considerations for the use of AI in the classroom are presented.
Figure 1
Magic Media Produces “Wizard Using A Laptop” To Illustrate AI-Wizardry

Note. Kendra Hart (2024) generated this image using the Canva Magic Media platform. I dedicate any rights I hold to this image to the public domain via CC0.
Introduction
The significance of student motivation as a determining factor in the learning process is well-documented (Urhahne & Wijnia, 2023). Motivation has been linked to academic success in technology-enhanced learning environments (Subbiah, 2024). Thus, keeping learners motivated ought to be a constant concern for instructional design professionals. Effective instructional design incorporates interest approaches to enhance learner motivation (Shanholtzer et al., 2019). For example, many educators will be familiar with techniques such as ‘attention grabbing,’ making student-content connections, and appealing to diverse learning styles. Keller (1987) proposed the ARCS Model of Instructional Design, which outlines four conditions for motivated learners including attention, relevance, confidence, and satisfaction (p.3). The look and feel of an online learning activity is an opportunity to make a first impression on a prospective learner. If a student feels intimidated by a wall of text or disinterested in the aesthetic of a page, their confidence and attention are compromised, and the student’s motivation to complete the learning activity may be threatened upon one glance at the content. Instructional designers are encouraged to learn graphic design strategies to boost learners’ visual engagement and motivation (Parsons, 2024). Visual literacy (Güney, 2019) and technology proficiency (Wang et al., 2021) have been identified as desirable skills for creating engaging instructional materials. Many instructional designers have a teaching background, and may still be developing these competencies for instructional design. Thankfully, Artificial Intelligence(AI)-powered toolkits can help these educators develop visually engaging materials and strength-based learning activities to boost student motivation.
Canva’s Magic Studio is a suite of AI-powered tools that aid instructional developers by dismantling barriers to effective visual design, and providing access to tools for learning activities that boost motivation in the domains of attention, relevance, confidence, and satisfaction. AI-enhanced features in Canva Magic Studio support instructional developers in creating professional presentations for diverse settings, clear audio tracks, and graphics including word art and audiovisual media (Figure 1). These tools allow creative professionals to bring colorful, complex, and visually engaging ideas to life without prerequisite skills in graphic and visual design. Additionally, Magic Studio tools are user-friendly and available to students, presenting opportunities for project-based learning. These assignments are promising for improving learner self-efficacy given the potential to boost creative outputs and allow students to play into their strengths, while AI-based tools enhance performance and confidence in areas for improvement. The Canva Magic Studio toolkit includes support for writing (Magic Write), presenting (Magic Design, AI-powered presenters), creating and editing (Magic Media), and more through compatible third-party apps.
Learning Objectives
Learning Objectives
- Read about the ARCS Model of Instructional Design
- Recognize how Canva Magic Studio supports student motivation in the domains of attention, relevance, confidence, and satisfaction.
- Evaluate the benefits and challenges of Canva Magic Studio for project-based learning.
- Reflect on responsible practices for the incorporation of AI-enhanced design tools in teaching and learning.
Case Study
About the ARCS Model
The ARCS Model of Instructional Design (Keller, 1987) identifies four categories which influence motivation to learn (Figure 2). Fulfilling requirements for attention entails initially capturing the learner’s interest, and sustaining this interest by arousing curiosity. The second component, relevance, is met when learners view learning objectives as personally significant and relating to goals. The third variable, confidence, describes learners’ expectations that they will succeed. Finally, learners obtain satisfaction when they accomplish goals, experience rewards, and feel proud of the product of their efforts. The case studies below illustrate how AI-enhanced tools such as Canva Magic Studio support fulfillment and motivation in each of the domains outlined by Keller.
Figure 2
Categories of the ARCS Model
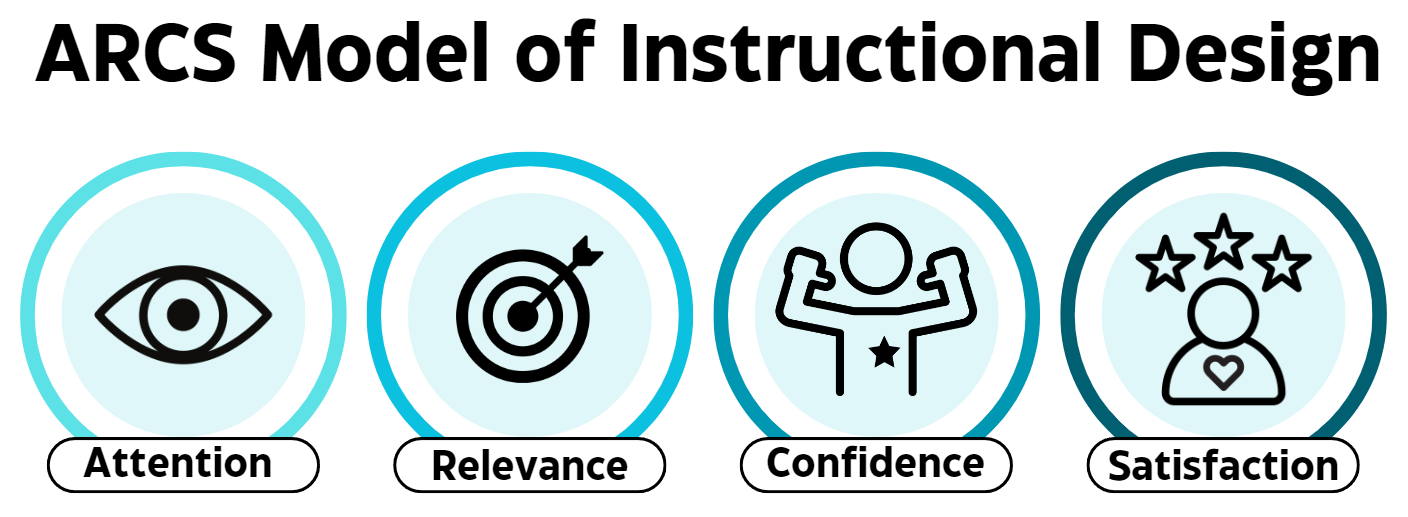
Note. This image was developed by Kendra Hart (2024) using the Canva design platform to reflect the domains of the ARCS Model of Instructional Design proposed by Keller (1987).
Supporting Attention with Canva Magic Studio
Vignette: Sunee
Sunee’s science teacher has tasked students with creating infographics about environmental conservation. Sunee understands that environmental conservation is important, but struggles to engage deeply with the project. Sunee writes some paragraphs including key facts for her infographic, but finds the content dull. In Canva, Sunee notices a bright pen icon next to the words “Magic Write.” She clicks the icon, and discovers options to modify the voice of her writing. The AI suggests ways to rephrase her points to communicate in different tones, including formal, fun, and whimsical. After trying out the “Sprinkle of Fairy Dust” option, which adds a whimsical twist to one of her paragraphs, Sunee gets the idea to create a poster displaying fairies advocating for the protection of their forest home. Excited by her new idea, Sunee searches the Canva media library for images of toadstools and fairies. She experiments with different colors and layouts for her design. She wants to add a picture of a damaged toadstool to illustrate the effects of pollution, but she can’t find an image on the web. The Magic Media tool allows her to generate an image to bring her idea to life! As Sunee works on her project, her understanding of the topic deepens. She is curious and excited by the AI-based tools in Canva. She has heard teachers discourage students from using AI in projects, but in a world that is increasingly driven by technology, Sunee understands that these tools will play an important role in the future of society. She is excited that the Magic toolkit has allowed her creativity to flourish with fewer limitations, and begins to consider how this tool could support her career aspirations in the field of digital marketing and design.
Keller (2016) describes the category of attention as “incorporat[ing] research on curiosity and arousal, interest, boredom, and other related areas such as sensation seeking” (p.4). Sunee’s story illustrates how Canva Magic Studio tools can spark and sustain students’ interest in learning projects. Visual interest and effective graphic design supports learner attention and absorption of content (Parsons, 2024). Canva Magic Studio includes a variety of AI-enhanced presentation and media creation tools to develop visually engaging resources for students and educators. Creative writing tools also spark students’ curiosity and creativity. The ability to smoothly transition between tone and template options provides learners with low-stakes opportunities to experiment with different presentation styles and formats. The option to frequently modify project aesthetics can help decrease under-stimulation and boredom in learners. Table 1 summarizes benefits of Canva Magic Studio for educators and students in the domain of attention.
Table 1
Benefits of Canva Magic Studio for Promoting Attention
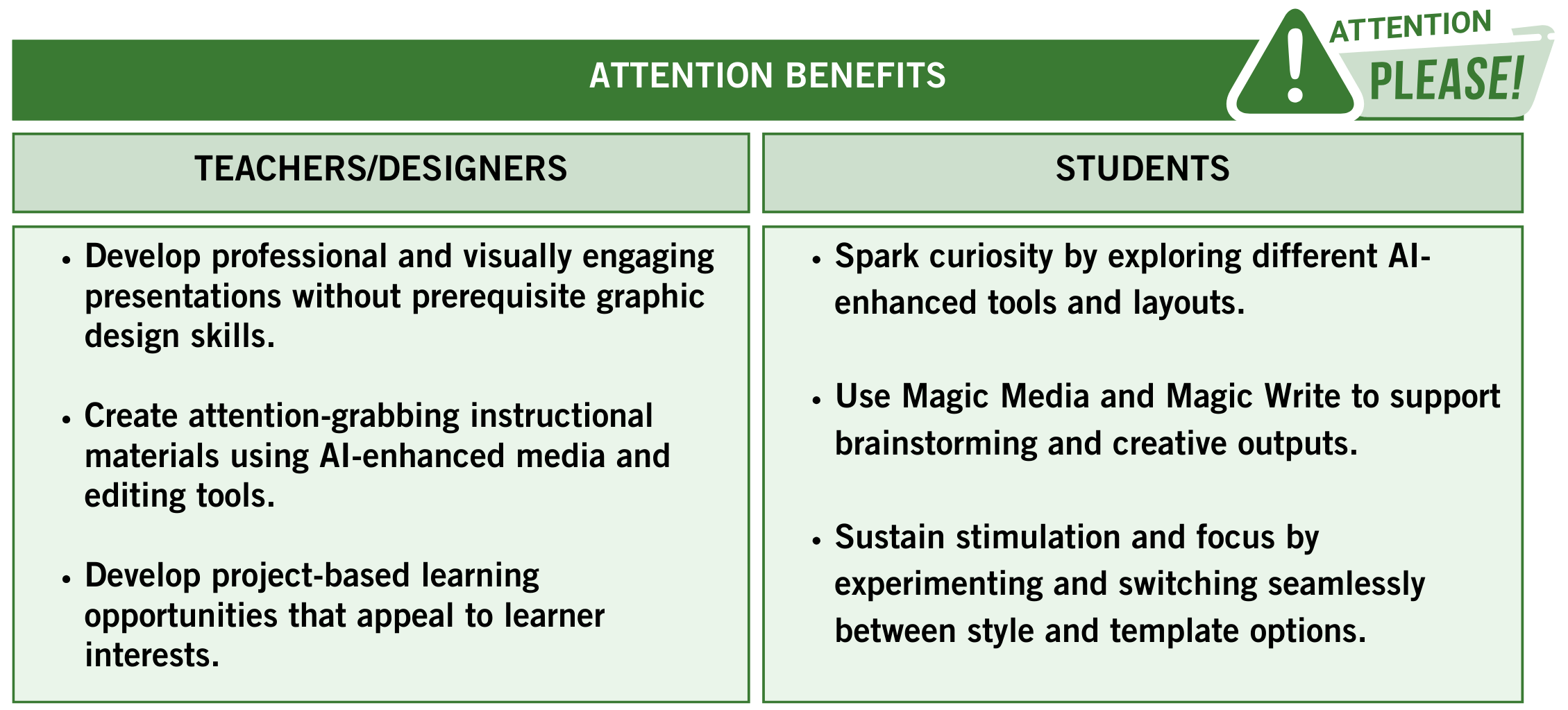
Note. The Magic_Motivation_Tables document includes alternate versions of each Table featured in this chapter in an accessible format. This table was designed by Kendra Hart (2024) using the Canva design platform.
Overtime, this ARCS model has been updated to reflect ongoing research in the instructional design field. In 2016, ARCS-V model, a new iteration, was described including a fifth category, volition (Keller, 2016). Volition relates to self-regulation and persistence (p.4). While attention-grabbing tools can support learner engagement, they also pose risks. For example, if motivation is boosted and volition is too-high, students can become overly anxious and struggle to identify when their work is complete (Keller, 2016). If students are too enthralled by AI-enhanced tools and visual aspects of their project, they may focus on aesthetic over content, becoming distracted from learning outcomes. While Canva Magic Studio reduces creative barriers and limitations, this can also present challenges for highly motivated students. If volition is too high, students may struggle to identify when they have done enough. These students may dedicate excessive time and energy to projects, leading to burnout or distraction from other study topics.
Supporting Relevance with Canva Magic Studio
Like many students living and studying in the Information Age, Sunee recognizes that AI-technologies will play an important role in the future that her schooling aims to prepare her for. For students who recognize how budding technologies relate to their futures, complete rejection of AI in the classroom could compromise their trust that learning activities adequately prepare them for goal achievement and long-term success. Technology acceptance in the classroom has been linked to improvements in self-regulated learning and motivation (An et al., 2023). Incorporation of AI tools allows educators and instructional designers to frame learning activities as opportunities to develop soft-skills for the future. Educators should make the relevance of these activities explicit to students through classroom activities and conversations.
Highlighting the Relevance of AI: Examples
Below are suggestions for learning activities to highlight the relevance of project-based learning using AI-enhanced tools.
Class Brainstorm:
- What are some current and future applications of Canva Magic Studio apps?
Written Reflection:
- How could you use Canva Magic Studio apps to support your personal or career goals?
Four-Corners Debate or Class Debate:
- Should AI-enhanced tools like Canva Magic Studio be permitted in the classroom? Why or why not?
- Is it cheating to use AI for school assignments? How do you know when it is acceptable?
Supporting Confidence with Canva Magic Studio
Vignette: Rahul
Rahul is a grade nine student who has qualified for his high school’s gifted program. He is passionate about learning and does well on tests. During high school orientation, Rahul learns that the gifted program uses project-based assessments instead of exams. Despite Rahul’s enthusiasm for learning, he lacks confidence in his design skills, which impacts his motivation to complete projects such as posters and presentations. After the orientation, Rahul asks his parents to take him out of the gifted program because he does not think he can succeed. Rahul’s parents encourage him to try the gifted program, and promise that if he doesn’t do well after the first semester, they will help him consider other options.
Rahul starts off the school year in a gifted history class. The final project involves making presentations in Canva. As Rahul explores the Canva platform, he is relieved to discover a variety of templates, design elements, and tools that are easy to use. Rahul selects a template that matches his topic. With the Magic Design tool, he can customize the layout and try out different styles without feeling overwhelmed. He adds images and word art, and considers different color suggestions made by the tool. Rahul uses the Magic Write feature in Canva to come up with a catchy and fun tagline for his presentation.
As Rahul works on his project, he notices that he is enjoying the process, and that the ease of using Canva Magic Studio has boosted his confidence. When Rahul finishes his presentation, he feels proud. When he presents his project to the class, the response is overwhelmingly positive. This experience has improved Rahul’s confidence and motivated him to take on more design challenges. Rahul decides to stay in the gifted program and continue to explore what AI-enhanced design tools have to offer.
Canva Magic Studio is a powerful tool for many bright students who, like Rahul, are able to absorb curriculum content but struggle with demonstrating learning through mediums such as artistic design. These tools allow students to lean into their strengths with fewer limitations, while simultaneously using AI to improve outcomes in skill areas where there is room for improvement. AI-tools offer alternative routes to success in areas such as formatting and presentation. By reducing barriers to success through supportive tools, Canva Magic Studio can improve accessibility, as well as students’ self-efficacy and willingness to persevere through challenges.
Table 2 outlines Magic Studio tools which can be implemented to boost success or enhance accessibility in different skill domains.
Table 2
Magic Studio Tools and Related Areas of Support

Note. The Magic_Motivation_Tables document includes alternate versions of each Table featured in this chapter in an accessible format. This table was designed by Kendra Hart (2024) using the Canva design platform.
Supporting Satisfaction with Canva Magic Studio
Students are more likely to demonstrate an interest in continued learning when they experience satisfaction or positive feelings in connection with learning activities (Keller, 2016). Canva Magic Studio tools reduce limitations on students’ strengths in areas such as design and creativity, allowing students to produce projects that let their talents shine and elicit a sense of pride. Educators can help students feel positive about their accomplishments by providing positive feedback and opportunities for students to showcase their best work through presentations or gallery walks.
Table 3 provides a summary of benefits and challenges for educators implementing Canva Magic Studio tools to boost motivation in the classroom.
Table 3
Summary: Benefits and Challenges of Canva Magic Studio
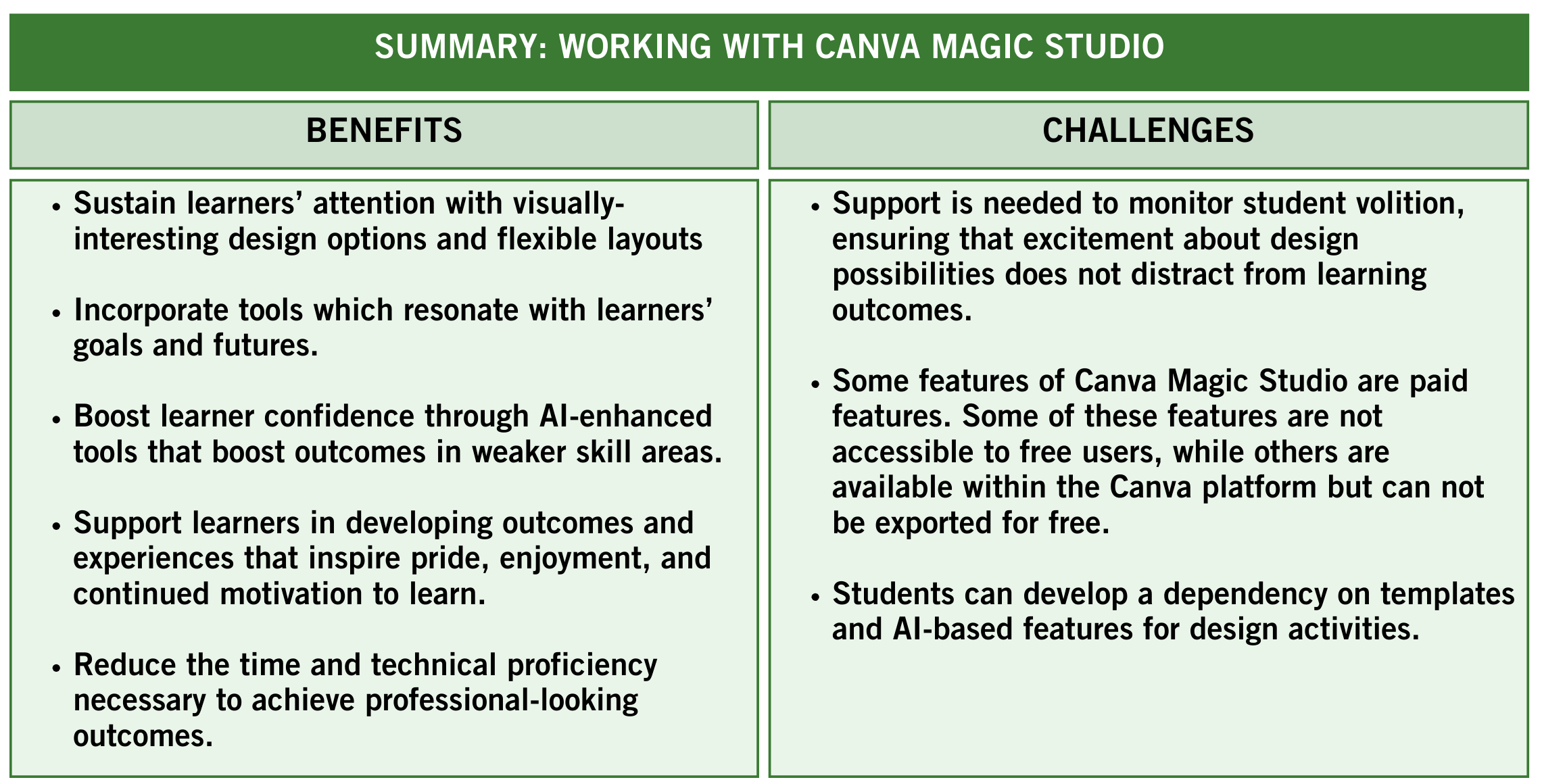
Note. The Magic_Motivation_Tables document includes alternate versions of each Table featured in this chapter in an accessible format. This table was designed by Kendra Hart (2024) using the Canva design platform.
Support for Using Canva Magic Studio in the Classroom
Click to access the ARC Evaluation resource, which offers guidance for evaluating the effectiveness of Canva Magic Studio to boost motivation in project-based learning activities.
The following tips , also outlined in Table 4, will help reduce challenges associated with Canva Magic Studio in the classroom.
- Help students recognize how the skills cultivated through use of AI-tools relate to their goals or futures through explicit instruction or reflection activities on the topic.
- To avoid challenges associated with distinctions between free and paid subscription features, clarify to students which features are available to them, and how you would like them to export or submit their designs.
- Assignments should encourage creative incorporation of Magic Studio tools, not dependency on them. Personal reflections on how AI tools were implemented can promote creativity and academic integrity.
- Provide supervision and support as students are learning how to use this tool. Effective supervision can help redirect students so that their time is used effectively, and their creative work remains oriented to fulfill learning goals. As students are learning to use the tool, support may be needed to promote confidence.
View Canva’s Teacher Guides for AI in the Classroom for online support implementing specific tools in your teaching practice.
Table 4
Practical Tips for Using Canva Magic Studio in the Classroom

Note. The Magic_Motivation_Tables document includes alternate versions of each Table featured in this chapter in an accessible format. This table was designed by Kendra Hart (2024) using the Canva design platform.
Responsible use of AI
Safe and responsible use of AI in the classroom requires educators to think critically about the risks and benefits of these tools. One benefit of Canva Magic Studio is that this set of features was designed with educators in mind, leading to improvements in support for instructors and safety protections for students (Canva, 2023b). Canva provides a Guide on How To Use Magic Studio Safely and Legally, acknowledging the risks associated with improper or irresponsible use of these tools. However, they have also published the results of their AI in Education study, which indicates that the benefits of AI for both teachers and students can outweigh challenges, if these features are used properly.
Andarwati et al. (2024) found that AI-tools, including features available in Canva, can help teachers in the domains listed below.
- Manage student data more effectively
- Support personalized/individualized learning experiences
- Provide ongoing feedback to students
- Recognize patterns to provide individual support and responsively adjust teaching methods
- Develop effective teaching strategies and activities with AI-suggestions
Teachers must be aware of the limitations of AI technology, and be prepared to provide instruction on best practices to avoid the formation of negative habits in relation to ethics and technology (p. 198).
Expand the categories in the accordion below to reflect on safe use of AI in your teaching practice.
Future Research and Innovation
As generative AI technology continues to evolve, Canva is emerging as a leader in the educational technology space. We may soon see Canva Magic Studio develop features specifically to support educators through AI tools for lesson planning, gamification, and creating assessments. The addition of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) features could allow students to design and explore virtual spaces for learning. Future iterations of Canva Magic Studio may include more sophisticated analytics for educators to monitor student progress, deliver feedback, and identify knowledge gaps. Canva currently includes features to support translation of designs into multiple languages (Maas, 2024). This tool may be further developed to aid educators in culturally and linguistically diverse classrooms.
Online communities offer support and resources for educators seeking to learn more about integrating Canva in the classroom. The Canva Communities Tab includes links to virtual spaces for teachers and education creators. Canva Design School also offers a range of resources and courses to support learning. Engage with these spaces to stay up-to-date on announcements and innovations in educational technology.
Summary
The video below offers a summary of key points in this chapter.
Listen closely, and try to answer the questions that pop-up in the upper-right corner as you watch!
Note. This video was produced by Kendra Hart (2024) using the Canva design platform. To view a transcript of this video, access the Magic Studio Transcript
Acknowledgements
Thank you to the graduate students of ETAD 873, especially Chris Weiman, who supported the development of this chapter through peer feedback and review. The Author acknowledges the use of artificial intelligence tools to enhance contributions for this chapter. Microsoft CoPilot supported initial brainstorming activities. Canva Magic Media was used to demonstrate the image generation capabilities of artificial intelligence tools. Canva Magic Write was used to improve parts of the script for the instructional video in this chapter by making suggestions for an engaging tone. An AI-voice from Eleven Labs was selected for narration of the instructional video.
Open Researcher and Contributor ID (ORCID)
Hart, Kendra. https://orcid.org/0009-0009-6667-3818
Kendra Hart is an English teacher and instructional resource developer completing a Master of Education with a special focus on Educational Technology and Design. Her research interests include preservice teacher mentorship, open educational resources, and reducing accessibility barriers with distance learning. She has developed a variety of open source instructional modules, as well as content for undergraduate, graduate, and professional development courses. She has contributed to the International Journal of Coaching and Mentoring in Education, as well as to textbooks on theories of teaching and learning, and the integration of metacognition in mathematics instruction.
References
An, F., Xi, L., & Yu, J. (2024). The relationship between technology acceptance and self-regulated learning: The mediation roles of intrinsic motivation and learning engagement. Education and Information Technologies, 29(3), 2605-2623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11959-3
Andarwati, R., Widodo, G. A., & Darmanto, E. (2024). Implementation of artificial intelligence in the form of Canva in the learning process in the digital era. Jurnal Scientia, 13(01), 190-200. https://doi.org/10.58471/scientia.v13i01
Canva. (2023a). Canva’s AI in Education Study: Teachers embrace power of AI. https://www.canva.com/newsroom/news/ai-education-survey/
Canva. (2024a). Canva Magic Media [AI image-generation tool]. https://www.canva.com/ai-image-generator
Canva. (2024b). Design school. https://www.canva.com/designschool/
Canva (2024c). How to use Magic Studio safely and legally. https://www.canva.com/help/using-magic-studio-safely-and-legally/
Canva (2023b). Introducing Canva’s biggest education launch. https://www.canva.com/newsroom/news/canva-for-education-new-tools/
Canva. (2024d). Join the community. https://www.canva.com/community/
Canva. (2024e) Teacher guides to wow your classroom with AI. https://www.canva.com/education/teaching-resources/classroom-ai-guides/
Güney, Z. (2019). Visual literacy and visualization in instructional design and technology for learning environments. European Journal of Contemporary Education, 8(1), 103-117. https://doi.org/10.13187/ejced.2019.1.103
Keller, J. M. (1987). Development and use of the ARCS model of instructional design. Journal of instructional development, 10(3), 2-10. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02905780
Keller, J. M. (2016). Motivation, learning, and technology: Applying the ARCS-V motivation model. Participatory Educational Research, 3(2), 1-15. http://dx.doi.org/10.17275/per.16.06.3.2
Maas, D. (Spring 2024). Found in translation. Alberta Teachers’ Association. https://teachers.ab.ca/news/found-translation
Microsoft. (2024). CoPilot. [Large language model]. https://copilot.microsoft.com/
Parsons, M. R. (2024). Message design for instructional designers – An introduction. In M. Ramlatchan (Ed.), Instructional Message Design: Theory, Research, and Practice (Vol. 3). Kindle Direct Publishing. https://digitalcommons.odu.edu/instructional_message_design_vol3/4
Shanholtzer, B. N., Thoron, A. C., Bunch, J. C., & Colclasure, B. C. (2019). Using interest approaches in instructional design and delivery. IFAS Extension. University of Florida. https://doi.org/10.32473/edis-wc334-2019
Subbiah, A. (2024). Enhancing learner motivation and academic achievement: The impact of the ARCS model of motivational design on technology-enhanced learning environments. In Recent trends and future direction for data analytics (pp. 270-288). IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/979-8-3693-3609-0.ch012
Urhahne, D., & Wijnia, L. (2023). Theories of motivation in education: An integrative framework. Educational Psychology Review, 35(2), Article 45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-023-09767-9
Wang, X., Chen, Y., Ritzhaupt, A. D., & Martin, F. (2021). Examining competencies for the instructional design professional: An exploratory job announcement analysis. International Journal of Training and Development, 25(2), 95-123. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijtd.12209
Instructional design: the process by which learning experiences are developed
Interest approaches: activities or strategies intended to improve student engagement, attention, and focus on learning
ARCS Model of Instructional Design: An instructional design model developed by John Keller (1987), which emphasizes the importance of attention, relevance, confidence, and satisfaction as factors influencing learner motivation.
Visual literacy: the ability to effectively interpret, evaluate, and create meaningful images from visual media
Volition: the power of determining, choosing, or having a will to do something.
Virtual Reality (VR): a computer-generated environment including immersive objects and scenes that make the user feel submerged in a different reality
Augmented Reality (AR): A virtual interactive experience that combines 3D computer-generated content with real-world images or features

