Tumor Cytology
Tumors are classified into two broad categories: epithelial and mesenchymal (Fig. 5.11). Epithelial cells form the skin and adnexal structures of the skin; lining of airways, intestines, genital and urinary tract; renal tubules; liver; and glandular tissues. Mesenchymal cells are subdivided into spindle cells and discrete round cells. Spindle cells form the body’s connective tissue, fat, muscle, bone, cartilage, and blood vessels. The discrete round cell category comprises mainly hemopoietic cells.
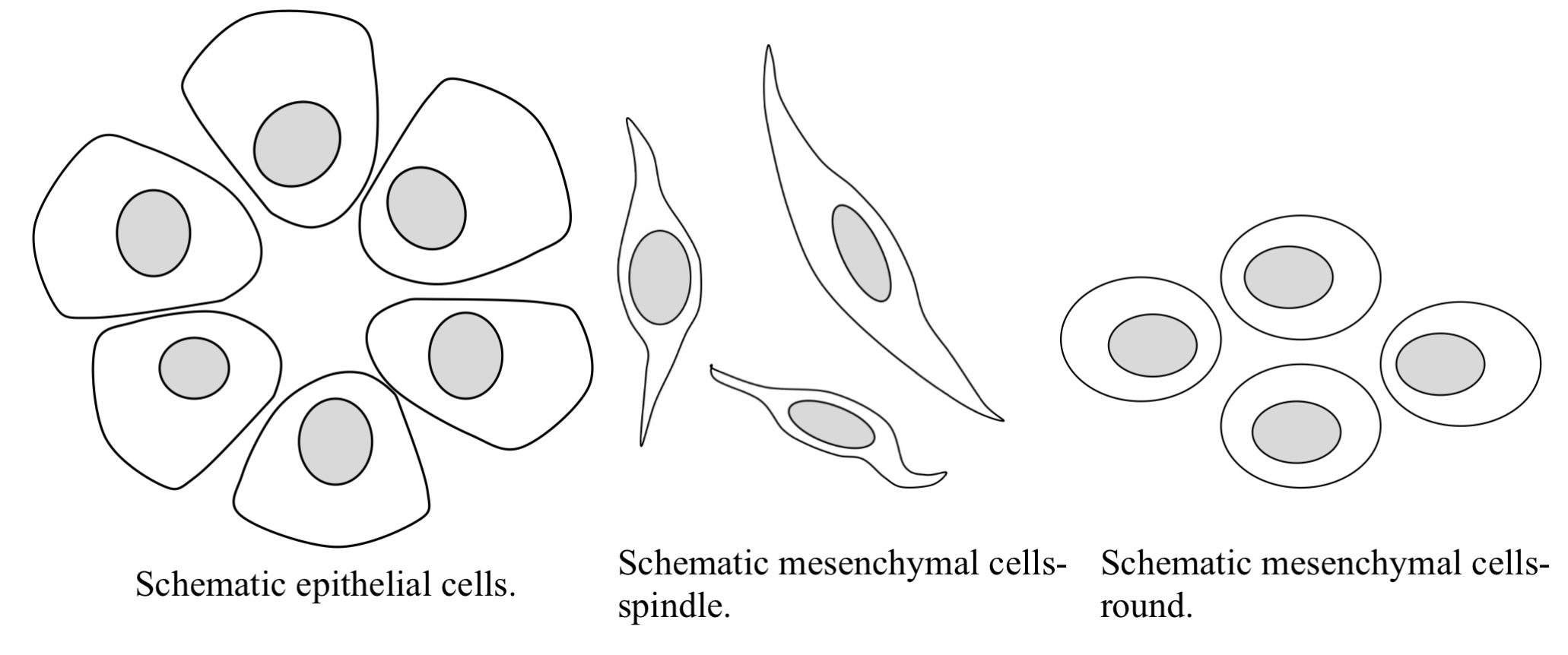
Cell forming connective tissue, fat, muscle, bone, lymphatics, andblood vessels.
Hemopoietic cell; also includes transmissible venereal tumor cells.

